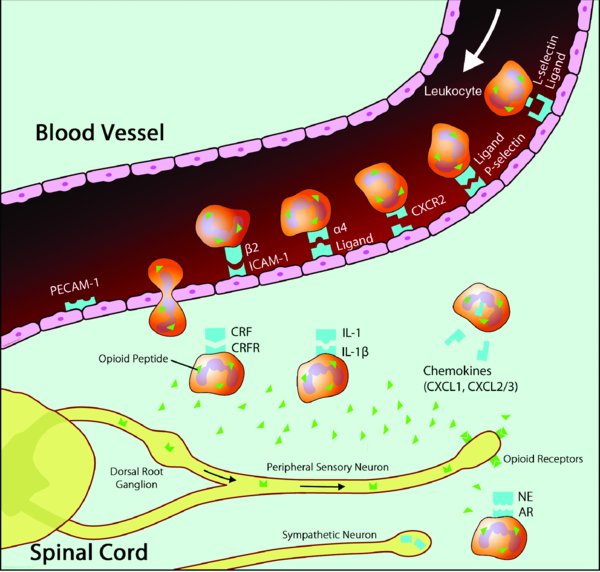
Opioid-containing leukocytes are attracted to inflamed tissue by various chemokines and cytokines. Specific upregulated protein facilitates leukocyte migration through the vascular endothelium. In the inflamed tissue, leukocytes interact with releasing agents such as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), interleukin-1 (IL-1), and norepinephrine (NE) derived from postganglionic sympathetic neurons to secrete opioid peptides. These bind to peripheral opioid receptors, synthesized in the dorsal root ganglia and transported to peripheral endings of sensory neurons, to mediate analgesia. AR = adrenergic receptor; CRFR = corticotropin-releasing factor receptor; ICAM = intercellular adhesion molecule; PECAM = platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule.