Sausage Fingers, Raynaud's Phenomenon and Thickening of the Skin (Systemic Sclerosis)
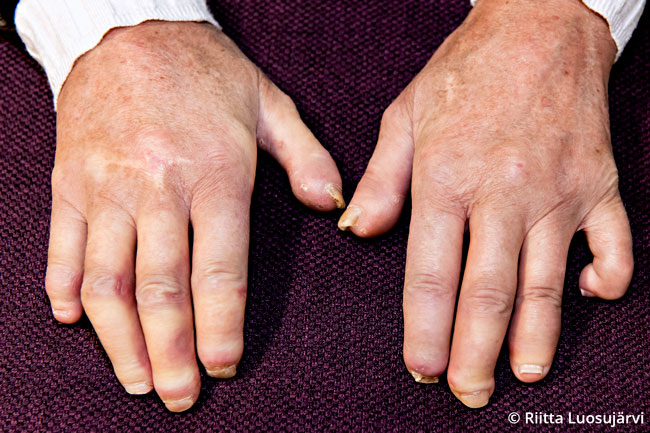
Sausage fingers, Raynaud's phenomenon and thickening of the skin in a patient with advanced systemic sclerosis. The skin is tightly attached to the underlying tissue. The fingers cannot be straightened or bent. Fatty tissue has been resorbed from the distal parts of the fingers, and the nails are deformed. There are calcium deposits at the tips of the thumbs. There is ulceration on fingers 2-4 of the right hand.
Picture and text: Riitta Luosujärvi
Primary/Secondary Keywords
- sausage fingers
- Raynaud
- skin thickening
- thick skin
- Raynaud's phenomenon
- Raynaud's syndrome
- systemic sclerosis
- scleroderma
- ulceration
- calcium deposit