Electrical Cardioversion
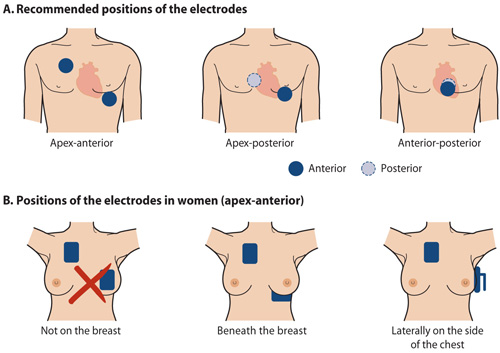
Electrical cardioversion. The electric current is best conducted through the heart if one of the defibrillator electrodes is positioned at the back of the patient (apex-posterior or anterior-posterior). If there is no such electrode available, it is recommended that one electrode is positioned at the apex of the heart and the other one up on the right side of the sternum (apex-anterior). In women, the electrode must not be positioned on the breast. Sufficient amount of conducting paste should be applied on the electrodes. Hand-held electrodes should be pressed on the skin with sufficient force. A biphasic defibrillator is used to perform cardioversion and the device's maximal energy is used already in the first cardioversion shock. A new cardioversion attempt can be performed immediately, as soon as the patient's blood pressure and atrial fibrillation rhythm have stabilized, i.e. in practice about one minute after the previous attempt. When cardioversion is performed in a patient with a pacemaker, the electrodes are positioned so that the axis between them is perpendicular to the axis between the pacemaker and the apex of the heart. In patients with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator, cardioversion is safest to perform by programming the device to give a synchronized intracardiac shock while the patient is under light anaesthesia. If this is not successful, cardioversion is performed like in a patient with a pacemaker. Picture source: .
Picture: Heikkilä J et al. (eds.) Kardiologia [Cardiology]. Duodecim Medical Publications 2008, page 544, text: The Finnish Medical Society Duodecim
Primary/Secondary Keywords
- Cardiology
- Cardioversion
- Electrical cardioversion
- Electrode
- Electrodes
- Position
- Defibrillator
- Defibrillation
- Atrial fibrillation
- AF