Erythema Migrans
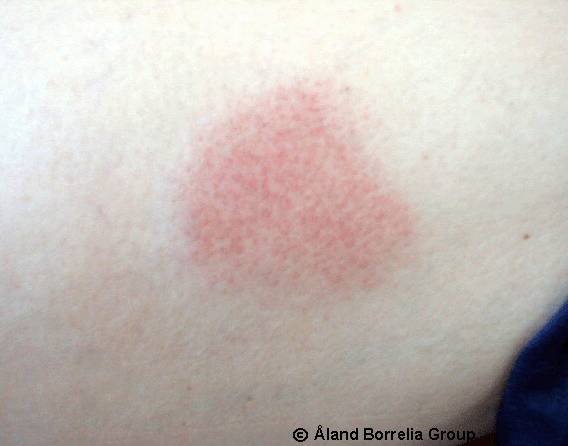
Erythema migrans. The tick bite occurred 14 days before the picture was taken. The patch (7 x 7 cm) has no pale central area any more, and it bears some resemblance to nummular eczema. Borreliosis (B. garinii) was verified (for research purposes) by culture from a biopsy taken from the lesion.
Picture: Åland Borrelia Group
Primary/Secondary Keywords