This section details the RDW with is a routine part of the Complete Blood Count (CBC) test.
The technical definition is:
RDW = (Standard deviation of red cell volume / MCV) × 100
The practical definition is:
The RDW is a test that indicates degree of variability between RBC sizes. An elevated RDW indicates substantial RBC size variability such as in early iron deficiency anemia where small RBC’s may be produced along with the pre-existing normal sized RBC’s. This will produce an elevated RDW as there is now two populations of RBC’s with different sizes.
The Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) is a statistical function that relates to the variability in the size of RBCs in circulation.
- Elevation of RDW is the earliest hematologic manifestation of iron deficiency anemia
- Heterozygous a or
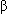 -thalassemia trait or lead poisoning give normal RDW values
-thalassemia trait or lead poisoning give normal RDW values - Two populations of cells (for example iron deficiency microcytic RBCs with a pre-existing population of normal sized RBCs will give a high RDW)
- Bimorphic population of microcytes and macrocytes will show normal MCV (Should examine the blood film and also note that the RDW will be highly increased in this scenario)
These RDW tests may be indicated for:
- Evaluation of Anemia
- Detection of a hematologic disorder, neoplasm or immunologic abnormality
- Determination of the presence of hereditary hematologic abnormalities
- Monitoring the effects of acute or chronic blood loss
- Monitoring hematologic status during pregnancy
- Monitoring patients with disorders associated with elevated or decreased erythrocyte counts
- Monitoring the progression of non-hematologic disorders associated with abnormal erythrocyte counts
- Adrenal dysfunction
- Bone marrow failure
- Cancers
- COPD
- Hypothyroidism
- Liver disease
- Malabsorption syndromes
- Renal disease
- Monitoring response to drugs or chemotherapy and to evaluate undesired reactions to drugs that may cause blood dyscrasias
Consult your laboratory for their normal ranges as these may vary somewhat from the ones listed below.
RDW normal is 11.5-14.5%
A normal RDW may be found in the following conditions:
I. MCV & RDW Normal
- Normal individual; no underlying disease
- Acute blood loss
- Anemia of chronic disease
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
- Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Hemolysis
II. MCV Decreased & RDW Normal
- Anemia of chronic disease
- Thalassemia
III. MCV Increased & RDW Normal
- Aplastic anemic
- Pre-leukemia
An elevated RDW (>14.5%) may be found in the following conditions:
I. MCV Normal & RDW Increased
- RDW increased before MCV becomes abnormal in early Vitamin B12, Iron or Folate deficiency
- Globinophathy (Anemic)
II. MCV Decreased & RDW Increased
- Iron deficiency anemia
- RBC fragmentation
- Hemoglobin H Disease
- Sideroblastic anemia
- Thalassemia intermedia
III. MCV & RDW Increased
- Alcohol abuse (independent of liver disease)
- Folate deficiency
- Hemolytic anemia (Immune)
- Liver disease
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
IV. Post Transfusion
- RDW often increased; MCV is variable
N/A
No significant clinical conditions are associated with decreased RDW.
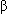 -thalassemia trait or lead poisoning give normal RDW values
-thalassemia trait or lead poisoning give normal RDW values