Hormones that Influence Blood Glucose Levels
| Hormone | Tissue of Origin | Metabolic Effect | Effect on Blood Glucose |
|---|---|---|---|
Insulin | Pancreatic 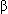 cells cells | 1. Enhances entry of glucose into cells 2. Enhances storage of glucose as glycogen, or conversion to fatty acids 3. Enhances synthesis of proteins and fatty acids 4. Suppresses breakdown of protein into amino acids; of adipose tissue, into free fatty acids | Lowers |
Somatostatin | Pancreatic D cells | 1. Suppresses glucagon release from 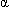 cells (acts locally) cells (acts locally)2. Suppresses release of insulin, pituitary tropic hormones, gastrin, and secretin | Lowers |
Glucagon | Pancreatic 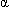 cells cells | 1. Enhances release of glucose from glycogen 2. Enhances synthesis of glucose from amino acids or fatty acids | Raises |
Epinephrine | Adrenal medulla | 1. Enhances release of glucose from glycogen 2. Enhances release of fatty acids from adipose tissue | Raises |
Cortisol | Adrenal cortex | 1. Enhances synthesis of glucose from amino acids or fatty acids 2. Antagonizes insulin | Raises |
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Anterior pituitary | 1. Enhances release of cortisol 2. Enhances release of fatty acids from adipose tissue | Raises |
Growth hormone | Anterior pituitary | 1. Antagonizes insulin | Raises |
Thyroxine | Thyroid | 1. Enhances release of glucose from glycogen 2. Enhances absorption of sugars from intestine | Raises |
From Sacher, RA, and McPherson, RA: Widmann's Clinical Interpretation of Laboratory Tests, ed 11. FA Davis, Philadelphia, 2000, p. 448, with permission.