Group A 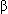 -hemolytic streptococci produce a variety of extracellular products capable of stimulating antibody production. Such antibodies do not act on the bacteria and have no protective effect, but their existence indicates recent active streptococci. Antibody production is most reliably noted in response to streptolysin O, and the test for this antibody is termed an antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer. Antibodies in response to hyaluronidase (AH), streptokinase (anti-SK), deoxyribonuclease B (ADN-B), and nicotinamide (anti-NADase) also can be produced. When ASO titers are low, tests for these latter antibodies can be produced to substantiate the diagnosis, because they are more sensitive tests.
-hemolytic streptococci produce a variety of extracellular products capable of stimulating antibody production. Such antibodies do not act on the bacteria and have no protective effect, but their existence indicates recent active streptococci. Antibody production is most reliably noted in response to streptolysin O, and the test for this antibody is termed an antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer. Antibodies in response to hyaluronidase (AH), streptokinase (anti-SK), deoxyribonuclease B (ADN-B), and nicotinamide (anti-NADase) also can be produced. When ASO titers are low, tests for these latter antibodies can be produced to substantiate the diagnosis, because they are more sensitive tests.
Elevated antistreptococcal antibody titers can occur in healthy carriers of 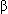 -hemolytic streptococci. Elevated levels also are seen in those with rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, bacterial endocarditis, scarlet fever, otitis media, and streptococcal pharyngitis.
-hemolytic streptococci. Elevated levels also are seen in those with rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, bacterial endocarditis, scarlet fever, otitis media, and streptococcal pharyngitis.
Nursing Care Before the Procedure
Client preparation is the same as that for any study involving the collection of a peripheral blood sample (see Appendix I).
- Medications that the client is currently taking or has recently taken should be noted, because therapy with antibiotics and adrenal corticosteroids may alter test results.
A venipuncture is performed and the sample collected in a red-topped tube. A capillary sample may be obtained in infants and children as well as in adults for whom a venipuncture may not be feasible. The sample must be handled gently and sent promptly to the laboratory.
Nursing Care After the Procedure
Care and assessment after the procedure are the same as for any study involving the collection of a peripheral blood sample.
- Abnormal values: Note and report increased levels of specific tests in relation to signs and symptoms of joint or renal disease. Assess for joint pain, elevated temperature, sore throat, and history of a recent infection. Administer ordered antipyretics, analgesics, and antibiotic therapy. Prepare for additional tests if more specificity is needed.
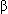 -hemolytic streptococci produce a variety of extracellular products capable of stimulating antibody production. Such antibodies do not act on the bacteria and have no protective effect, but their existence indicates recent active streptococci. Antibody production is most reliably noted in response to streptolysin O, and the test for this antibody is termed an antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer. Antibodies in response to hyaluronidase (AH), streptokinase (anti-SK), deoxyribonuclease B (ADN-B), and nicotinamide (anti-NADase) also can be produced. When ASO titers are low, tests for these latter antibodies can be produced to substantiate the diagnosis, because they are more sensitive tests.
-hemolytic streptococci produce a variety of extracellular products capable of stimulating antibody production. Such antibodies do not act on the bacteria and have no protective effect, but their existence indicates recent active streptococci. Antibody production is most reliably noted in response to streptolysin O, and the test for this antibody is termed an antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer. Antibodies in response to hyaluronidase (AH), streptokinase (anti-SK), deoxyribonuclease B (ADN-B), and nicotinamide (anti-NADase) also can be produced. When ASO titers are low, tests for these latter antibodies can be produced to substantiate the diagnosis, because they are more sensitive tests.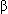 -hemolytic streptococci. Elevated levels also are seen in those with rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, bacterial endocarditis, scarlet fever, otitis media, and streptococcal pharyngitis.
-hemolytic streptococci. Elevated levels also are seen in those with rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, bacterial endocarditis, scarlet fever, otitis media, and streptococcal pharyngitis.