Classifications of Hemolytic Anemias
- Abnormalities of the RBC membrane
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Hereditary elliptocytosis
- Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis
- Hereditary stomatocytosis and xerocytosis
- Inherited erythrocyte enzyme disorders
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
- Other enzyme deficiencies
- Disorders of hemoglobin production
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Sickle cell syndromes
- Sickle cell disease
- Sickle cell trait
- HbS
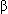 -thalassemia syndrome
-thalassemia syndrome - Hemoglobin C disease
Disorders of hemoglobin production
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Sickle cell syndromes
- Sickle cell disease
- Sickle cell trait
- HbS
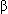 -thalassemia syndrome
-thalassemia syndrome - Hemoglobin C disease
- Methemoglobins/hemoglobin M
- Unstable hemoglobin
- Thalassemia syndromes
- Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
- Microangiopathic and macroangiopathic hemolytic anemia
- Chemical and toxic agents
- Infections causing hemolysis
- Hypersplenism
- Systemic disorders
- Primary
- Secondary (associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphomas, and carcinomas)
- Drug induced
- Infections
From Sacher, RA, and McPherson, RA: Widmann's Clinical Interpretation of Laboratory Tests, ed 10. FA Davis, Philadelphia, 1991, p 94, with permission.