The adrenal medulla, a component of the sympathetic nervous system, secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine, which are collectively known as the catecholamines. A third catecholamine, dopamine, is secreted in the brain, where it functions as a neurotransmitter.
Epinephrine (adrenalin) is secreted in response to generalized sympathetic stimulation, hypoglycemia, or arterial hypotension. It increases the metabolic rate of all cells, heart rate, arterial blood pressure, and levels of blood glucose and free fatty acids, and it decreases peripheral resistance and blood flow to the skin and kidneys.
Norepinephrine is secreted by sympathetic nerve endings, as well as by the adrenal medulla, in response to sympathetic stimulation and the presence of tyramine. It decreases the heart rate, while increasing peripheral vascular resistance and arterial blood pressure. Normally, norepinephrine is the predominant catecholamine.
The only clinically significant disorder involving the adrenal medulla is the catecholamine-secreting tumor, pheochromocytoma. Catecholamine-producing tumors also can originate along sympathetic paraganglia; these tumors are known as functional paragangliomas. Pheochromocytomas may release catecholamines, primarily epinephrine, continuously or intermittently. Because the most common sign of pheochromocytoma is arterial hypertension, measurement of plasma catecholamines (or the urinary metabolites thereof) is indicated in evaluating new-onset hypertension.55
| Conventional Units | SI Units |
|---|
| Epinephrine and norepinephrine | 100-500 ng/L | |
| Epinephrine |
| Supine | 0-110 pg/mL | 0-600 pmol/L |
| Standing | 0-140 pg/mL | 0-764 pmol/L |
| Norepinephrine |
| Supine | 70-750 pg/mL | 413-4432 pmol/L |
| Standing | 200-1700 pg/mL | 1,182-10,047 pmol/L |
Note: Results are usually evaluated in relation to urinary measurements of catecholamine metabolites. Several measurements of plasma levels may also be indicated.
Nursing Care Before the Procedure
General client preparation is the same as that for any study involving the collection of a peripheral blood sample (see Appendix I).
- For this test, the client should fast for 12 hours and abstain from smoking for 24 hours before the test. Vigorous exercise should be avoided, with provision made for rest in a recumbent position for at least 1 hour before the study.
- Medications that may alter test results, especially over-the-counter cold preparations containing sympathomimetics, may be withheld for up to 2 weeks before the test, although this practice should be confirmed with the person ordering the study.
- The need for dietary restriction of amine-rich foods for 48 hours before the test should be confirmed with the laboratory performing the test or the person ordering it.
- If samples are to be obtained via an intermittent venous access device (e.g., heparin lock), the client should be informed of its purpose and that it may be inserted as long as 24 hours before the test.
If more than one sample is to be obtained, a heparin lock should be inserted 12 to 24 hours before the test; the stress of repeated venipunctures could falsely elevate levels.
- For hospitalized individuals, a sample of venous blood should be collected in a chilled lavender-topped tube between 6 and 8 AM. For nonhospitalized clients, the first sample should be obtained after approximately 1 hour of rest in a recumbent position. The sample is handled gently to avoid hemolysis, packed in ice, and sent to the laboratory immediately.
- The client should then be helped to stand for 10 minutes, after which a second sample is obtained. The time(s) of collection and the position of the client should be noted on the laboratory request form.
Nursing Care After the Procedure
If an intermittent venous access device was inserted, remove after completion of the test and apply a pressure bandage to the site.
- Resume foods and any medications withheld before the test, as well as usual activities.
- Abnormal levels: Note increased levels in relation to 24-hour urinary vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and metanephrine levels. Assess for pulse and blood pressure increases, hyperglycemia, shakiness, and palpitations associated with increased values.
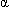 -methyldopa, hydralazine, quinidine, and isoproterenol (Isuprel) may produce elevated levels.
-methyldopa, hydralazine, quinidine, and isoproterenol (Isuprel) may produce elevated levels.