Tolbutamide (Orinase) is a hypoglycemic agent that produces hypoglycemia by stimulating the 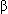 cells of the pancreas to secrete and release insulin. An IV infusion of tolbutamide raises the serum insulin and causes a rapid decrease in the blood glucose level. Thus, the test demonstrates the pancreatic
cells of the pancreas to secrete and release insulin. An IV infusion of tolbutamide raises the serum insulin and causes a rapid decrease in the blood glucose level. Thus, the test demonstrates the pancreatic 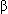 -cell response to drug-induced stimulation. Note that the test can be performed with glucagon or leucine instead of tolbutamide for clients who are sensitive to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides.
-cell response to drug-induced stimulation. Note that the test can be performed with glucagon or leucine instead of tolbutamide for clients who are sensitive to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides.
Nursing Alert
- Because of the expected drop in blood sugar levels, the test should be performed with extreme caution, if at all, on individuals with fasting blood sugars of 50 mg/dL or less.
- If the client is allergic to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides, the test should be performed using glucagon or leucine instead of tolbutamide.
Nursing Care Before the Procedure
Client preparation is essentially the same as that for an OGTT.
- The individual should be informed that venous access will be established with either a continuous infusion or an intermittent device and that a medication that lowers blood sugar will be administered.
- The client should be questioned regarding allergies to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides.
- Clients with a history of abnormal hypoglycemia will need reassurance that they will be monitored closely during the test.
Venous access is established and a sample is obtained for a fasting blood sugar (FBS). The IV catheter is then connected to an intermittent device (e.g., heparin lock) or to a continuous IV infusion of normal saline at a keep-vein-open (KVO) rate. Tolbutamide 1.0 g mixed in 20 mL sterile water is administered IV. Blood glucose samples are obtained via the IV catheter at 15-minute intervals for the first hour and then at 1½-, 2-, and 3-hour intervals. Observe the client closely for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. If hypoglycemia occurs, obtain a stat FBS, notify the physician, and initiate an IV infusion of 5 percent glucose and water, if ordered.
Note any signs or symptoms of sensitivity reaction to tolbutamide. If a reaction occurs, notify the physician and administer drugs as ordered. Maintain an open IV line until there is no further danger of adverse drug reaction.
Nursing Care After the Procedure
The venous access device is left in place until any danger of hypoglycemia is past. It is then removed and a pressure bandage applied to the site. Food and medications withheld before the test, as well as usual activities, should be resumed on its completion.
- Continue to observe for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia for 2 hours or more, depending on results of the 3-hour interval blood sugar.
- Assess the venipuncture site for signs of hematoma or phlebitis.
- Observe for adequate intake when foods are resumed.
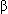 cells of the pancreas to secrete and release insulin. An IV infusion of tolbutamide raises the serum insulin and causes a rapid decrease in the blood glucose level. Thus, the test demonstrates the pancreatic
cells of the pancreas to secrete and release insulin. An IV infusion of tolbutamide raises the serum insulin and causes a rapid decrease in the blood glucose level. Thus, the test demonstrates the pancreatic 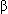 -cell response to drug-induced stimulation. Note that the test can be performed with glucagon or leucine instead of tolbutamide for clients who are sensitive to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides.
-cell response to drug-induced stimulation. Note that the test can be performed with glucagon or leucine instead of tolbutamide for clients who are sensitive to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides.