Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a glycoprotein that is unique to the developing placenta. Its presence in blood and urine has been used for decades to detect pregnancy. Tests using rabbits, frogs, and rats, however, have now been replaced by immunologic tests that use antibodies to hCG. Earlier immunologic tests were not always reliable, because the antibody used could cross-react with other glycoprotein hormones such as luteinizing hormone. Furthermore, it was sometimes not possible to obtain reliable results until 4 to 8 weeks after the first missed period. Currently, more sensitive and specific tests use antibody that reacts only with the 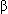 subunit of hCG, not with other hormones. The most sensitive of the radioimmunoassays for hCG can detect elevated levels within 8 to 10 days after conception, even before the first missed period.
subunit of hCG, not with other hormones. The most sensitive of the radioimmunoassays for hCG can detect elevated levels within 8 to 10 days after conception, even before the first missed period.
Because hCG is associated with the developing placenta, it is secreted at increasingly higher levels during the first 2 months of pregnancy, declines during the third and fourth months, and then remains relatively stable until term. Levels return to normal within 1 to 2 weeks of termination of pregnancy. Human chorionic gonadotropin prevents the normal involution of the corpus luteum at the end of the menstrual cycle and stimulates it to double in size and produce large quantities of estrogen and progesterone. It is also thought to stimulate the testes of the male fetus to produce testosterone and to induce descent of the testicles into the scrotum.
