During the first 10 weeks of life, the major serum protein is not albumin, but 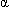 -fetoprotein (AFP). Fetal liver synthesizes huge quantities of AFP until about the 32nd week of gestation. Thereafter, synthesis declines until, at 1 year of age, the serum normally contains no more than 30 ng/mL.
-fetoprotein (AFP). Fetal liver synthesizes huge quantities of AFP until about the 32nd week of gestation. Thereafter, synthesis declines until, at 1 year of age, the serum normally contains no more than 30 ng/mL.
Resting liver cells (hepatocytes) normally manufacture very little AFP, but rapidly multiplying hepatocytes resume synthesis of large amounts.40 Thus, the test's greatest usefulness is in monitoring for recurrence of hepatic carcinoma or metastatic lesions involving the liver. Note that 30 to 50 percent of Americans with liver cancer do not have elevated AFP levels. More consistent elevations are seen in those Asian and African populations with a very high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma.41
Measurement of AFP levels in maternal blood and amniotic fluid is used to detect certain fetal abnormalities, especially neural tube defects such as anencephaly, spina bifida, and myelomeningocele (see Chapter 10 - Amniotic Fluid Analysis). Routine prenatal screening includes determination of the mother's serum AFP level at 13 to16 weeks of pregnancy. If maternal blood levels are elevated on two samples obtained 1 week apart, an ultrasound may be performed, and AFP levels in amniotic fluid may be analyzed. Other possible causes of elevated AFP levels during pregnancy include multiple pregnancy and fetal demise.