Measurement of C-peptide, which is accomplished through radioimmunoassay techniques, provides an index of 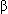 -cell activity that is unaffected by the administration of exogenous insulin. As the
-cell activity that is unaffected by the administration of exogenous insulin. As the 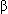 cells release insulin, they also release equimolar amounts of metabolically inactive C-peptide. Injectable insulin preparations are purified to remove C-peptide. Furthermore, injected insulin elevates immunoreactive serum insulin levels and suppresses pancreatic secretion of endogenous insulin and C-peptide. That is, although exogenous insulin elevates serum insulin levels, C-peptide levels are either unaffected or decreased. C-peptide determinations may be carried out to augment or confirm results of serum insulin measurements.59
cells release insulin, they also release equimolar amounts of metabolically inactive C-peptide. Injectable insulin preparations are purified to remove C-peptide. Furthermore, injected insulin elevates immunoreactive serum insulin levels and suppresses pancreatic secretion of endogenous insulin and C-peptide. That is, although exogenous insulin elevates serum insulin levels, C-peptide levels are either unaffected or decreased. C-peptide determinations may be carried out to augment or confirm results of serum insulin measurements.59