Ceruloplasmin (Cp) is an 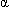 2-globulin that binds copper for transport within the circulation after it is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Among the disorders associated with abnormal ceruloplasmin levels is Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration), an inherited disorder characterized by excessive absorption of copper from the gastrointestinal tract, decreased ceruloplasmin, and deposition of copper in the liver, brain, corneas (Kayser-Fleischer rings), and kidneys. In addition to low ceruloplasmin levels, serum copper levels are decreased because of excessive excretion of unbound copper in the kidneys and deposition of copper in the body tissues. The disorder manifests during the first three decades of life and is fatal unless treatment is instituted.
2-globulin that binds copper for transport within the circulation after it is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Among the disorders associated with abnormal ceruloplasmin levels is Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration), an inherited disorder characterized by excessive absorption of copper from the gastrointestinal tract, decreased ceruloplasmin, and deposition of copper in the liver, brain, corneas (Kayser-Fleischer rings), and kidneys. In addition to low ceruloplasmin levels, serum copper levels are decreased because of excessive excretion of unbound copper in the kidneys and deposition of copper in the body tissues. The disorder manifests during the first three decades of life and is fatal unless treatment is instituted.
Other causes of abnormal ceruloplasmin levels are listed in Table 5-6.
Nursing Care Before the Procedure
Client preparation is the same as that for any test involving collection of a peripheral blood sample (see Appendix I).
A venipuncture is performed and the sample collected in a red-topped tube. Some laboratories require that the sample be placed in ice immediately on collection. The sample should be handled gently to avoid hemolysis and sent promptly to the laboratory.
Nursing Care After the Procedure
Care and assessment after the procedure are the same as for any study involving the collection of a peripheral blood sample.
- Abnormal values: Note and report decreased levels. Assess for hepatic or neurological or psychiatric manifestations of Wilson's disease. Assess for history of ceruloplasmin deficiency by Kayser-Fleischer rings determined by slit-lamp examination. Inform of need for follow-up medical care and genetic counseling.
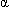 2-globulin that binds copper for transport within the circulation after it is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Among the disorders associated with abnormal ceruloplasmin levels is Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration), an inherited disorder characterized by excessive absorption of copper from the gastrointestinal tract, decreased ceruloplasmin, and deposition of copper in the liver, brain, corneas (Kayser-Fleischer rings), and kidneys. In addition to low ceruloplasmin levels, serum copper levels are decreased because of excessive excretion of unbound copper in the kidneys and deposition of copper in the body tissues. The disorder manifests during the first three decades of life and is fatal unless treatment is instituted.
2-globulin that binds copper for transport within the circulation after it is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Among the disorders associated with abnormal ceruloplasmin levels is Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration), an inherited disorder characterized by excessive absorption of copper from the gastrointestinal tract, decreased ceruloplasmin, and deposition of copper in the liver, brain, corneas (Kayser-Fleischer rings), and kidneys. In addition to low ceruloplasmin levels, serum copper levels are decreased because of excessive excretion of unbound copper in the kidneys and deposition of copper in the body tissues. The disorder manifests during the first three decades of life and is fatal unless treatment is instituted.