Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), formerly known as glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (GPT), catalyzes the reversible transfer of an amino group between the amino acid, alanine, and 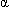 -ketoglutamic acid. Hepatocytes are virtually the only cells with high ALT concentrations, although the heart, kidneys, and skeletal muscles contain moderate amounts.
-ketoglutamic acid. Hepatocytes are virtually the only cells with high ALT concentrations, although the heart, kidneys, and skeletal muscles contain moderate amounts.
Elevated serum ALT levels are considered a sensitive index of liver damage resulting from a variety of disorders and numerous drugs, including alcohol. Elevations also may be seen in nonhepatic disorders such as muscular dystrophy, extensive muscular trauma, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure (CHF), and renal failure, although the increase in ALT produced by these disorders is not as great as that produced by conditions affecting the liver.
This test was formerly known as the serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) test.
| Conventional Units | SI Units |
|---|
| 10-30 U/L | 0.17-0.51 µkat/L |
| 1-36 U/L | 0.02-0.61 µkat/L |
| 5-35 U/L | 0.08-0.60 µkat/L |
| 5-25 U/L | 0.08-0.43 µkat/L |
| 8-50 U/L | 0.14-0.85 µkat/L |
| 4-36 U/L | 0.07-0.61 µkat/L |
Note: Reference values vary among laboratories and according to the method used for reporting results.
Nursing Care Before the Procedure
General client preparation is the same as that for any study involving collection of a peripheral blood sample (see Appendix I).
- For this test, the client should abstain from alcohol for at least 24 hours before the study.
- Because many drugs may alter ALT levels, a medication history should be obtained. It is recommended that drugs that may alter test results be withheld for 12 hours before the test, although this practice should be confirmed with the person ordering the study.
A venipuncture is performed and the sample is collected in a red-topped tube. The sample should be handled gently to avoid hemolysis and transported promptly to the laboratory.
Nursing Care After the Procedure
Care and assessment after the procedure are the same as for any study involving the collection of a peripheral blood sample.
- Resume any drugs withheld before the test.
- Abnormal levels: Note and report increased levels. Assess symptoms of liver dysfunction associated with increases such as jaundice, anorexia, and fatigue. Relate increases to other liver function tests. Provide rest and interventions to conserve energy. Tell client which drugs to avoid and encourage client to eat a healthy diet.
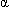 -ketoglutamic acid. Hepatocytes are virtually the only cells with high ALT concentrations, although the heart, kidneys, and skeletal muscles contain moderate amounts.
-ketoglutamic acid. Hepatocytes are virtually the only cells with high ALT concentrations, although the heart, kidneys, and skeletal muscles contain moderate amounts.