Glucagon is secreted by the 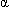 cells of the islets of Langerhans in response to decreased blood glucose levels. Its actions are opposed by insulin. Elevated glucagon levels are associated with conditions that produce actual hypoglycemia or a physiological need for greater blood glucose (e.g., trauma, infection, starvation, excessive exercise) and with insulin lack. Thus, elevated glucagon levels may be found in severe or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, despite hyperglycemia.
cells of the islets of Langerhans in response to decreased blood glucose levels. Its actions are opposed by insulin. Elevated glucagon levels are associated with conditions that produce actual hypoglycemia or a physiological need for greater blood glucose (e.g., trauma, infection, starvation, excessive exercise) and with insulin lack. Thus, elevated glucagon levels may be found in severe or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, despite hyperglycemia.
Nursing Care Before the Procedure
General client preparation is the same as that for any test involving collection of a peripheral blood sample (see Appendix I).
- For this test, the client should fast from foods for 8 hours before the study. Water is permitted.
A venipuncture is performed and the sample is collected in either a green- or a lavender-topped tube, depending on the laboratory performing the test. The sample should be handled gently to avoid hemolysis and sent to the laboratory immediately.
Nursing Care After the Procedure
Care and assessment after the procedure are the same as for any test involving the collection of a peripheral blood sample.
- Resume usual diet as soon as possible after the sample has been obtained.
- Complications and precautions: Assess the test results in relation to insulin and glucose levels.
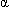 cells of the islets of Langerhans in response to decreased blood glucose levels. Its actions are opposed by insulin. Elevated glucagon levels are associated with conditions that produce actual hypoglycemia or a physiological need for greater blood glucose (e.g., trauma, infection, starvation, excessive exercise) and with insulin lack. Thus, elevated glucagon levels may be found in severe or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, despite hyperglycemia.
cells of the islets of Langerhans in response to decreased blood glucose levels. Its actions are opposed by insulin. Elevated glucagon levels are associated with conditions that produce actual hypoglycemia or a physiological need for greater blood glucose (e.g., trauma, infection, starvation, excessive exercise) and with insulin lack. Thus, elevated glucagon levels may be found in severe or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, despite hyperglycemia.