Figure 1
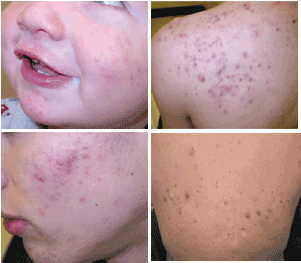
Inflammatory disorder of pilosebaceous follicles with a 90% prevalence in adolescence and young adulthood.
Etiology: Abnormal follicular keratinization, increased sebum 2° to androgens, Propionibacterium acnes (bacteria), inflammation.
Genetic factors; occlusive cosmetic agents; medications: steroids, ACTH, androgens, danazol, iodides, lithium, antiepileptics, oral contraceptives; diseases: congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS); worse with emotional stress.
History: Often asymptomatic lesions (especially comedones), although can be tender (nodules).
Physical: Two types of lesions, predominantly affect face, neck, chest and back.
- Noninflammatory—open ("black heads") and closed ("white heads") comedones.
- Inflammatory—papules, pustules, cysts, nodules; deep lesions leave scars, inflammatory papules, pustules & nodules on back and check with early scarring.
DDx: Folliculitis, perioral dermatitis, rosacea
Investigations: If irregular periods, hirsutism, virilization, or not responding to conventional therapy, work-up to rule out virilizing tumor or PCOS.
See Topic(s):