Population: Adolescents or young adults with acne.
Organizations
 AAD 2016, NICE 2021
AAD 2016, NICE 2021
Recommendations
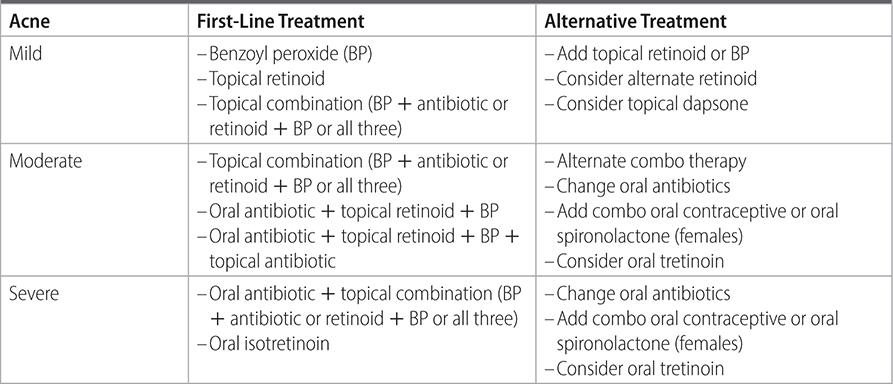
–See Table 32–1 for treatment recommendations based on severity.
–Oral antibiotics: prefer doxycycline or minocycline over tetracycline. Do not use in pregnant women or children <8 y of age; instead consider erythromycin or azithromycin.
–Use topical dapsone 5% gel for postinflammatory dyspigmentation.
–Consider oral contraceptives (OCDs) for inflammatory acne in females.
–Consider spironolactone in females.
–If adrenal hyperandrogenism, consider low-dose oral corticosteroids.
–Data are limited for pulsed dye laser, glycolic acid peels, salicylic acid peels.
–Consider intralesional corticosteroids injections in treatment of individual acne nodules.
–Complementary/Alternative therapy: topical tea tree can be used, but study is limited.
–No specific dietary changes are supported by data; high glycemic index diet and skim milk may influence acne.
–Skin care advice:
• Use skin pH neutral or slightly acidic wash twice daily.
• Do not use oil-based or comedogenic skin care products, sunscreens, makeup.
• No picking or scratching lesions.
Practice Pearls
• BP is effective in prevention of bacterial resistance.
• Do not use topical antibiotics as monotherapy because of risk of bacterial resistance.
• Topical adapalene, tretinoin, and BP are safely used in preadolescent children.
• Use systemic antibiotics for shortest duration and do not use as monotherapy without topicals.
• Monitor LFTs, serum cholesterol and triglycerides, depression, and IBD while on isotretinoin. Females should be counseled on contraceptive methods.
• Remember that OCP cannot be used in all patients.
TABLE 32–1 TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ACNE
Sources
–J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75(4):945-973.