Population: Children and adolescents without diagnosis of hypertension.
Organizations
 AAP 2017, NHLBI 2012, AAFP 2018, USPSTF 2020
AAP 2017, NHLBI 2012, AAFP 2018, USPSTF 2020
Screening Recommendations


Practice Pearls
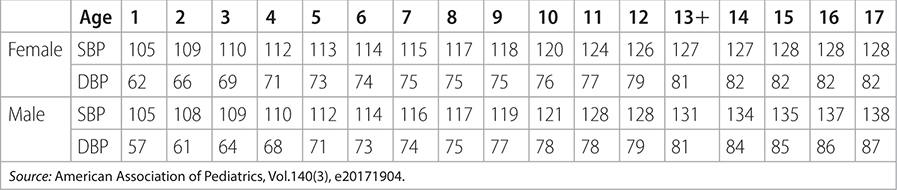
• Hypertension: average systolic blood pressure (SBP) or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 95th percentile for sex, age, and height on 3 or more occasions. See Table 13–3 and Ch. 33 for more detail.
• Counsel children and adolescents who have been diagnosed with hypertension regarding lifestyle modifications including diet and physical activity.
• Prescribe pharmacologic therapy to children and adolescents who fail lifestyle modifications.
• USPSTF concludes that the evidence to support screening for high BP in children and adolescents is insufficient and that the balance of benefits and harms cannot be determined.
TABLE 13–3 CUTOFFS FOR PEDIATRIC STAGE 1 HYPERTENSION
Sources
–Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e2017-e1904.
–NHLBI. Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents. 2012.
–NHLBI. A Pocket Guide to Blood Pressure Management in Children. 2012.
–AAFP. High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. 2018.
–USPSTF. Screening for High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. 2020.