The CDC maintains updated guidelines athttps://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/
Organizations
 CDC 2022, WHO 2021, WHO 2022, IDSA 2022, ACP 2023
CDC 2022, WHO 2021, WHO 2022, IDSA 2022, ACP 2023
Recommendations
–Offer symptomatic management including antipyretics, analgesics, and antitussives, encourage adequate nutrition and rehydration.
–Consider educating about breathing exercises.
–Counsel about signs and symptoms that warrant urgent medical care.
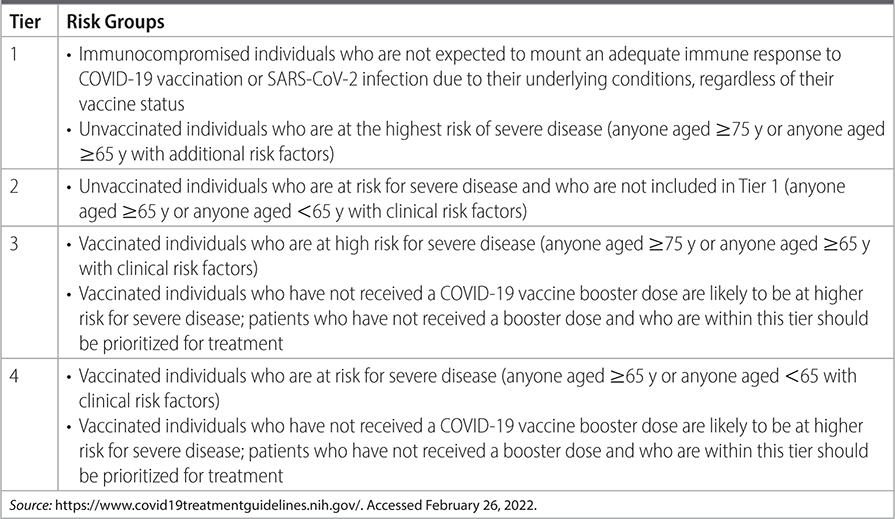
–Monoclonal antibody therapy: If at risk for progression to severe disease, offer monoclonal antibody therapy. See Tables 26–1 and 26–2 for risk tiers and comorbid conditions that elevate risk.
• CDC: use one of the following, listed in order of preference: ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir, sotrovimab, remdesivir, molnupiravir.
• WHO: use casirivimab, imdevimab, or sotrovimab.
–In patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 at high risk for progression to severe, give nirmatrelvir/ritonavir within 5 d of symptom onset (300-mg nirmatrelvir/100-mg ritonavir BID × 5 d, GFR 30–60 mL/min/1.73 m2 150 mg/100 mg BID ×5 d, GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 not recommended) OR remdesivir within 7 d of symptom onset (200 mg day 1 followed by 100 mg on days 2 and 3, pediatric dosing 5 mg/kg on day 1 and 2.5 mg/kg on days 2 and 3).
–In patients with no other treatment options (can’t use above options) who are at high risk for progression to severe disease, give FDA-qualified high titer COVID-19 convalescent plasma within 8 d of symptom onset or molnupiravir within 5–7 d of symptom onset (800 mg daily × 5 d only in nonpregnant patients ≥18 y).
TABLE 26–1 CDC PATIENT RISK GROUPS FOR PRIORITIZING COVID THERAPY
–Outside the United States in areas where predominant variants are susceptible in moderate to severely immunocompromised individuals, give pre-exposure prophylaxis with tixagevimab/cilgavimab (150 mg/150 mg IM ×1 dose) for patients in whom vaccination is not likely to be adequate or possible.
–Corticosteroids:
• Do not use for patients not requiring hospitalization or supplemental oxygen.
• If discharged from hospital without supplemental oxygen, stop steroids.
• If discharged from hospital with supplemental oxygen, insufficient evidence exists to guide decision.
–Consider home pulse ox monitoring for pts safe for discharge home with risk factors for progression to severe disease.
–Do not use fluvoxamine outside of clinical trials given currently limited data.
–Do not use inhaled corticosteroids for ambulatory patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in absence of other indications.
–Do not use chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, HIV protease inhibitors, famotidine, colchicine, nitazoxanide, ciclesonide, or antibiotic therapy in the absence of other indications.
–Do not use anticoagulants or antiplatelet therapy in outpatients in the absence of other indications.
–Do not stop ACE inhibitors, statin therapy, NSAIDs, or corticosteroids being used for comorbid conditions.
–See Table 23–3 for guidance on other unproven therapies.
TABLE 26–2 MEDICAL CONDITIONS THAT INCREASE RISK OF PROGRESSION TO SEVERE COVID
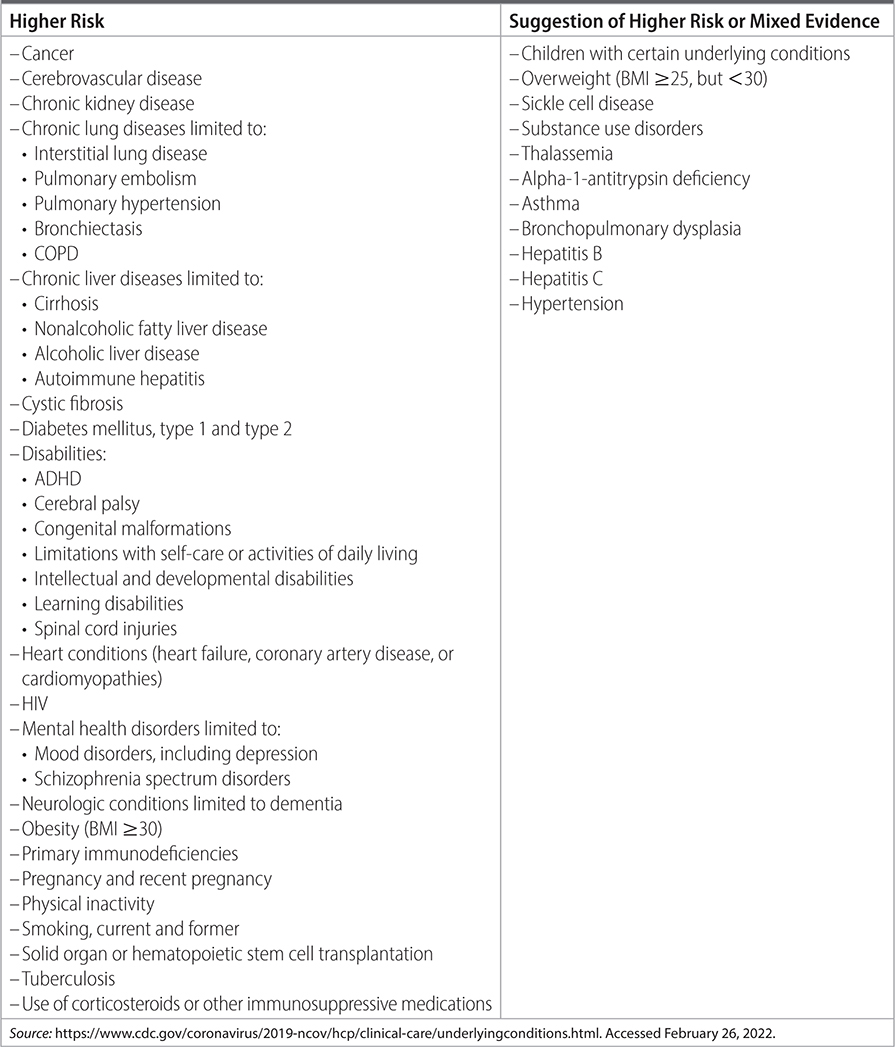
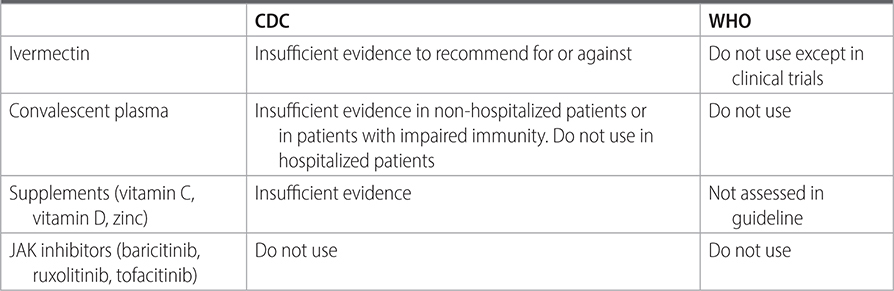
TABLE 26–3 COMPARISON OF RECOMMENDATIONS FOR VARIOUS THERAPIES IN NONSEVERE DISEASE, IN THE NON-HOSPITAL SETTING
Practice Pearls
• Convalescent plasma showed reduction in hospitalizations and medical visits, however unclear evidence given limited events, may be more effective if containing high titers of neutralizing antibodies and used earlier in presentation.
• Remdesivir reduced hospitalizations and medical visits up to day 28.
• Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir resulted in reduced all-cause mortality and fewer COVID-related hospitalizations, but contraindication with drugs highly dependent on CYP3A clearance or potent CYP3A inducers and should check all drug interactions before initiation (no studies in children).
• Molnupiravir showed reduction in COVID-related mortality and COVID-related hospitalizations (not recommended in children due to possible effects on bone and cartilage growth).
• When deciding between outpatient treatment options, consider age, symptom duration, renal function, drug interactions, product availability. No data exist for combining these treatment options.
• In the United States, neutralizing antibody treatments were found to be largely inactive against the most common variants and are no longer recommended for pre- or postexposure prophylaxis or for treatment.
• In susceptible areas tixagevimab/cilgavimab was shown to have reduction in symptomatic COVID-19 infection within 6 mo.
• Bacterial co-infection was found to be uncommon and procalcitonin was not an effective tool for discontinuing antibiotics compared to clinical judgment. WBC and CRP were shown to decrease in patients with bacterial infections compared to COVID-19 and may be a useful guide for antibiotic discontinuation.
• Limited studies exist on outcomes for children, but remdesivir and corticosteroids are commonly used given low risk of adverse events and recent studies support use of remdesivir down to patients weighing 3.5 kg.
Sources
–https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed February 26, 2022.
–BMJ. 2020;370:m3379.