Population: Adults who are acutely ill.
Organizations
 NICE 2019, VA/DoD 2019, KDIGO 2012
NICE 2019, VA/DoD 2019, KDIGO 2012
Prevention Recommendations
–General care of the acutely ill patient.
• In the absence of hemorrhagic shock, use isotonic crystalloids rather than colloids for intravascular volume expansion.
• Do not use diuretics to prevent or treat AKI except in the management of volume overload.
• Do not use low-dose dopamine in either the prevention or treatment of AKI.
• Use vasopressors in addition to fluids for management of vasomotor shock with or at risk for AKI. Avoid the combination of ACE/ARB, diuretics, and NSAIDs. This combination is more likely to cause AKI, especially in those >75 y of age and with preexisting renal impairment.
Practice Pearls
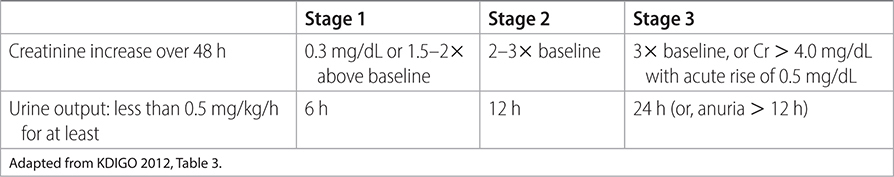
• AKI is defined as any of the following:
- The increase in SCr by ≥0.3 mg/dL over 48 h.
- Increase in SCr to ≥1.5 times baseline within the past 7 d.
- Urine volume < 0.5 mL/kg/h for 6 h.
• Stages of AKI and corresponding lab values (Table 10–1).
Sources
–NICE. Acute Kidney Injury: Prevention, Detection and Management of Acute Kidney Injury up to the Point of Renal Replacement Therapy. London, UK: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2019. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng148
–VA/DoD. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care. Washington, DC: Department of Veterans Affairs, Department of Defense; 2019.
–Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury: Kidney International Supplements; March 2012;2(1).
TABLE 10–1 STAGES OF ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
Population: Adults receiving intravenous iodinated contrast.
Organizations
 NICE 2019, VA/DoD 2019, KDIGO 2012
NICE 2019, VA/DoD 2019, KDIGO 2012
Prevention Recommendations
–Consider IV volume expansion to at-risk adults, including those with:
• CKD with eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2.
• Heart failure.
• Age 75 y or older.
• History of renal transplant.
• Use of a large volume of contrast medium.
• Intra-arterial administration of contrast medium with first-pass renal exposure.
• Consider temporarily stopping ACE inhibitors and ARBs in adults having iodine-based contrast media if they have chronic kidney disease with an eGFR < 40 mL/min/1.73 m2.
• Inconsistent evidence for N-acetylcysteine use to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy.
–Consult a pharmacist to assist with drug dosing in adults or children at risk for AKI.
Sources
–NICE. Acute Kidney Injury: Prevention, Detection and Management of Acute Kidney Injury up to the Point of Renal Replacement Therapy. London, UK: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2019. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng148
–VA/DoD. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care. Washington, DC: Department of Veterans Affairs, Department of Defense; 2019.
–Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury: Kidney International Supplements. 2012;2(1).