Clinical Importance of Methylguanine Methyltransferase.
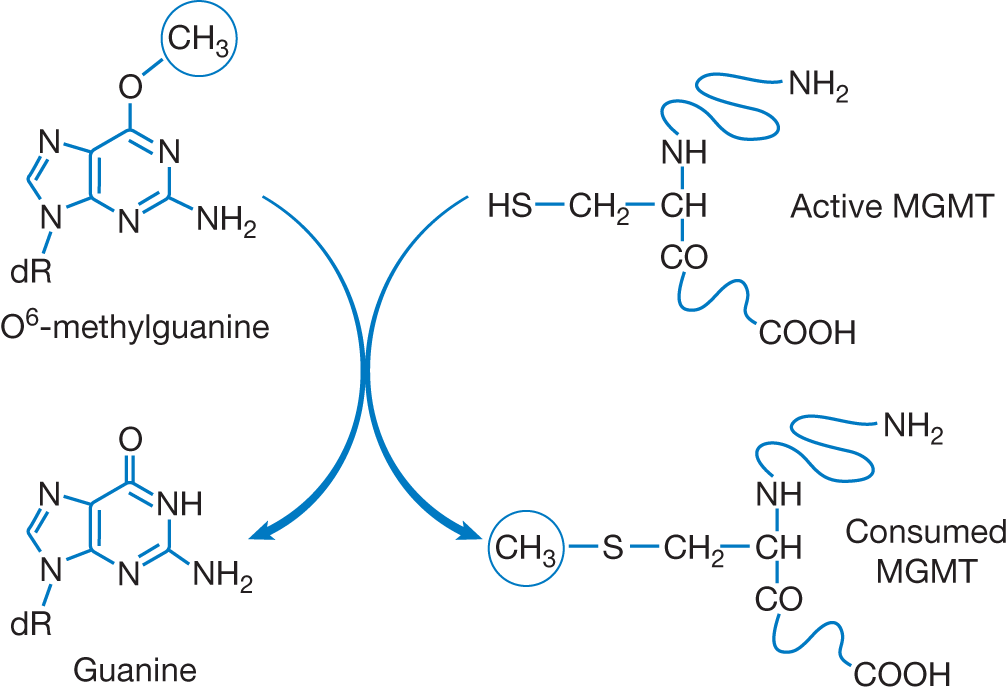
The DNA repair protein O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) plays an important role in response to alkylating agents. The protein demethylates DNA, and hence does undo the effect of alkylating agents such as temozolamide. Epigenetic silencing through promoter methylation of the MGMT gene impairs this repair process and increases temozolamide-induced cell death. Clinical studies have shown MGMT silencing by promoter methylation is associated with temozolamide sensitivity in CNS tumors and longer survival for patients. Temozolomide induces severe lymphopenia; hence, prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii to prevent pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is warranted.