Ethylenimines.
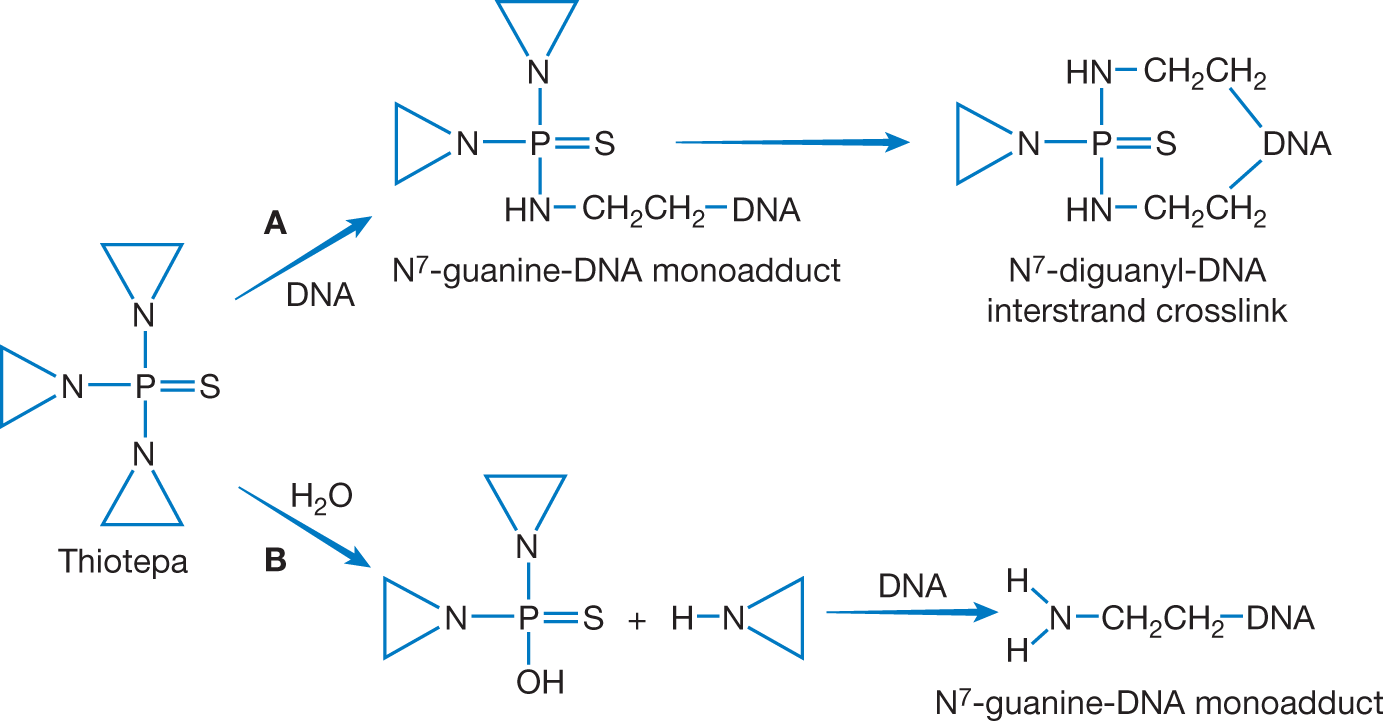
Thiotepa has three aziridine rings, which are susceptible to nucleophilic attack from DNA resulting in interstrand crosslinking as well as single-base methyl adduction. The unstable aziridine rings are similar to those seen during metabolism of nitrogen mustards. Thiotepa is used to reduce the risk of graft rejection when used in conjunction with high-dose busulfan and cyclophosphamide as a preparative regimen for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for pediatric patients with beta-thalassemia. It is also used for controlling intracavitary effusions secondary to diffuse or localized neoplastic diseases of various serosal cavities and for treatment of superficial papillary carcinoma of the urinary bladder. It can cause cutaneous toxicity; hence, the skin should be cleansed at least twice daily through 48 hours after the last dose of thiotepa.