Antifolate Mechanism of Action.
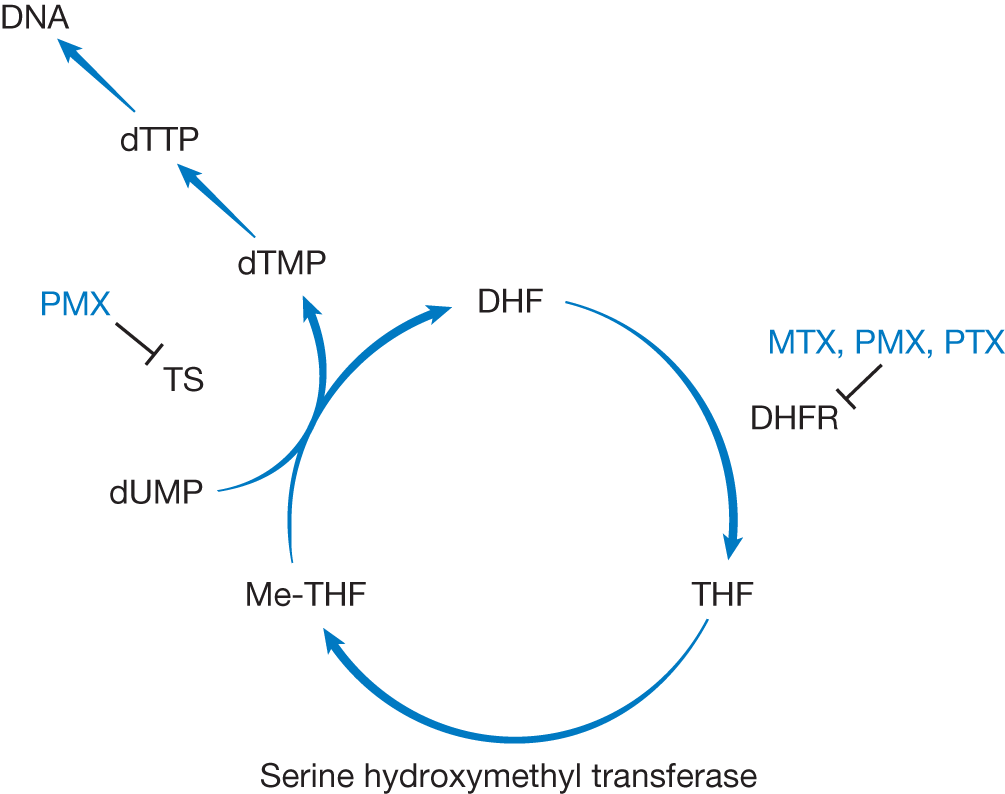
First-generation antifolate drugs are exemplified by methotrexate (MTX). It acts primarily by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), the enzyme responsible for reducing DHF and producing one-carbon recipients. Second-generation antifolate drugs are exemplified by pemetrexed (PMX). In addition to DHFR, PMX also inhibits thymidylate synthase (TS) and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase (GARFT), resulting in a distinct (from MTX) spectrum of antifolate activity, more directly affecting pyrimidine and purine precursors.