Ribonucleotide Reductase Inhibition
| DRUG and COMMON INDICATIONS | MECHANISM OF ACTION | CLINICAL POINTS |
|---|---|---|
Hydroxyurea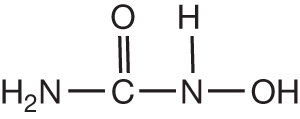
| Inhibits RNR, which is responsible for converting ribonucleotide diphosphates to deoxyribonucleotides, in particular, it targets the RNR-M2 subunit. In sickle cell disease, hydroxyurea increases hemoglobin F (HbF) via intermittent cytotoxic suppression of erythroid progenitors that affects kinetics of erythropoiesis leading to recruitment of erythroid progenitors with increased HbF levels. Free radical formation, iron chelation, activation of soluble guanylyl cyclase, and direct nitric oxide production are among other mechanisms of action for HbF induction by hydroxyurea |
|
CML, chronic myeloid leukemia.