Polyglutamate “trapping” of methotrexate (MTX).
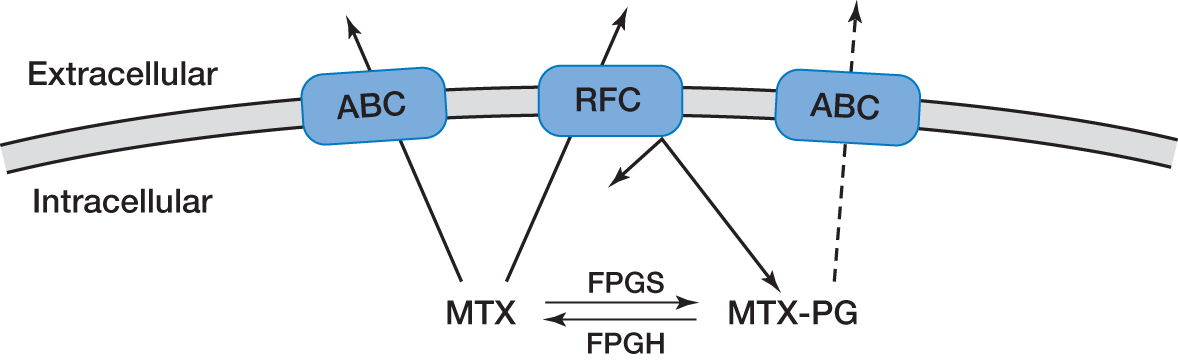
Once in the cell, folate can be polyglutamated with multiple glutamate groups via the enzyme FPGS to form polyglutamylated folates (F-PG). Polyglutamation of certain antifolate drugs occurs, for example, MTX + (Glutamate)n→ MTX-PG. The polyglutamate addition to these molecules makes the modified target significantly more polar, reducing its affinity for folate transporters, effectively “trapping” the antifolate drugs within cells, thereby providing a large intracellular reservoir of drug and enhancing its cytotoxic activity. Various efflux proteins, including various subtypes of ABC, may remove MTX and MTX-PG from within the cell, but in vitro data suggest that MTX-PG has significantly reduced binding affinity compared to MTX. ABC, ATP binding cassette efflux protein; FPGH, folylpolyglutamyl hydrolase; FPGS, folylpolyglutamyl synthetase.