| DRUG and COMMON INDICATIONS | MECHANISM OF ACTION | CLINICAL POINTS |
|---|
Cytarabine (ara-C)
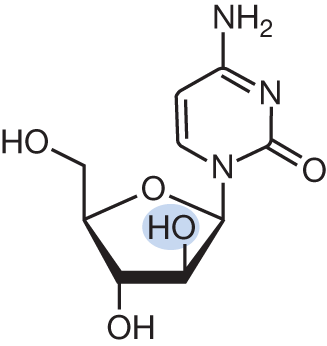
- AML
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- CML in blast crisis
- CNS leukemia
- Primary CNS lymphoma
- NHL
| Cytarabine mimics cytosine and is metabolized through the pathway below. Of note, Ara-U and Ara-UMP are inactive metabolites
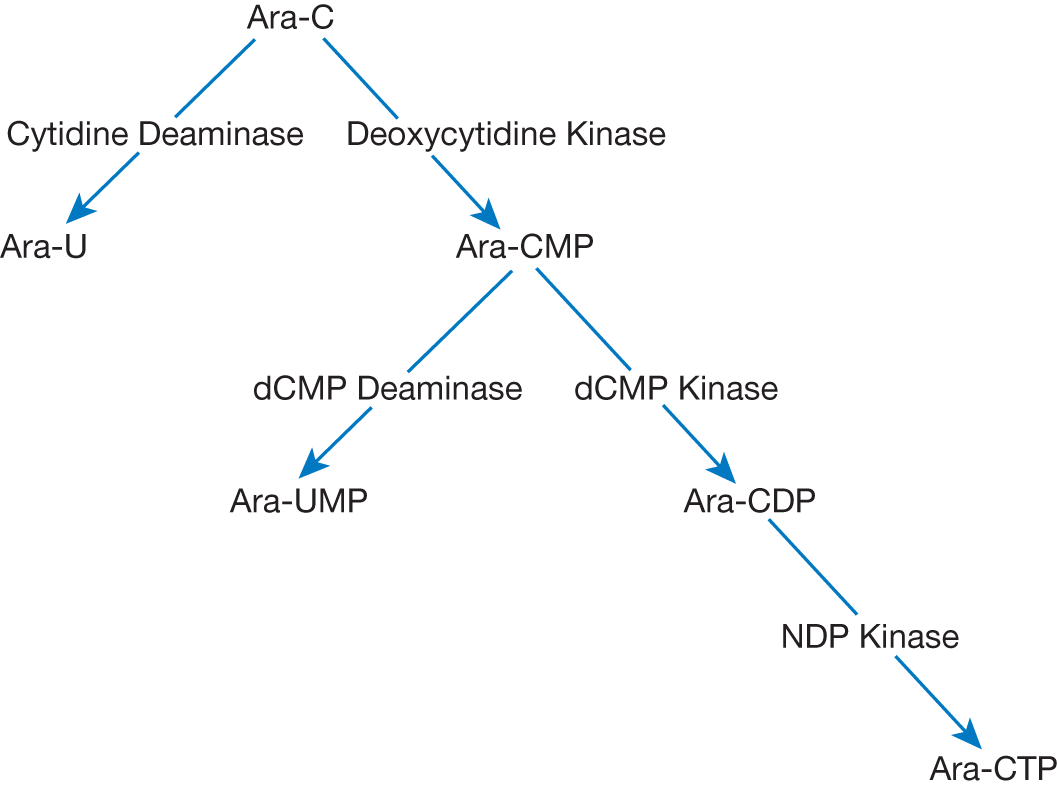
Cytarabine affects DNA synthesis in the following ways:
- Inhibition of DNA polymerase A and B for replication and repair
- Incorporated into DNA to inhibit template function and chain elongation
| - Intravenous (IV) administration. Can also be given intrathecally for prevention or treatment of CNS leukemia/lymphoma
- The majority of the dose (70%–80%) is excreted in urine. Dose adjustment in renal impairment advised, especially in the setting of high-dose ara-C (HiDAC)
- Consider dose adjustment in severe hepatic impairment
- Adverse events include at all doses:
- Myelosuppression
- Gastrointestinal toxicities (nausea/vomiting, mucositis, diarrhea)
- Hepatic dysfunction (increased liver function tests [LFTs], intrahepatic cholestasis)
- Cytarabine syndrome (fever, myalgia, bone pain, chest pain, rash)
- Pancreatitis
- Maculopapular rash
- Adverse events include particularly at high doses (>1,000 mg/m2):
- CNS→ acute cerebellar toxicity, unsteady gait, dementia, coma
- Gastrointestinal: gastrointestinal (GI) ulcer, pancreatitis, peritonitis
- Ocular: conjunctivitis or keratitis. Corneal deposits presenting as photophobia, foreign body sensation, mild-to-moderate vision loss. For moderate- and high-dose regimens, corticosteroid eye drops must be given throughout cytarabine treatment and up to 72 hours posttreatment
- Pulmonary toxicities: pulmonary edema, pneumonia
|
Fluoropyrimidines (5-Fluorouracil [5-FU] and prodrugs capecitabine and tegafur)
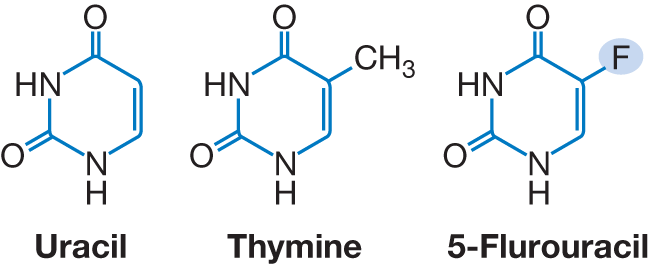
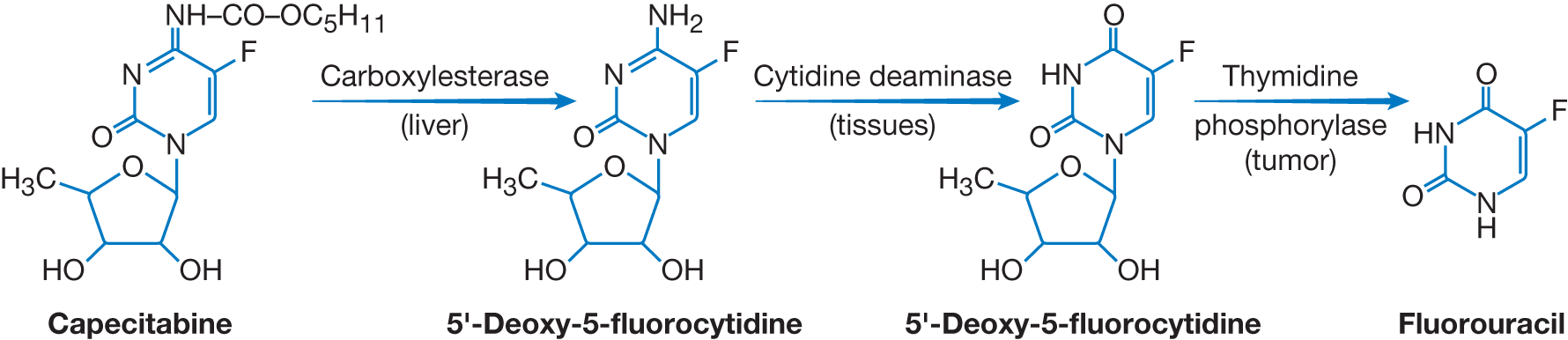
- Gastrointestinal cancers
- Breast
- Ovarian
| Fluoropyrimidines are analogs of uracil and thymine and inhibit both RNA and DNA (major mechanism) synthesis. Fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP), the active metabolite of the prototype 5-FU binds to thymidylate synthase (TS), which normally catalyzes the conversion of dUMP to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). The resultant fluorodeoxythymidine monophosphate (FdTMP) is triphosphorylated and incorporated into DNA, subsequently causing single=strand breaks and termination of DNA replication.
The binding of FdUMP is stabilized by leucovorin, the reduced from of folate. See Chapter 4, Antimetabolites: Antifolates, for further discussion of folic acid metabolism and its role in the conversion of dUMP to dTMP. | - Administered IV or orally
- Renal excretion, requiring dose modification in the presence of reduced glomerular filtration rates
- Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) is the initial and rate-limiting enzyme in the catabolism of 5-FU; patients with a DPD deficiency are at risk of developing severe 5-FU-associated toxicity
- Adverse events include:
- Myelosuppression
- GI toxicities (nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, oral mucositis)
- Hepatotoxicity
- Cardiotoxicity (coronary vasospasm, QT prolongation)
- Cerebellar toxicity
|
Gemcitabine
- Monotherapy in pancreatic cancer
- + Paclitaxel in breast cancer
- + Carboplatin in ovarian cancer
- + Cisplatin in NSCLC
- + Cisplatin in bladder cancer
- Cervical
- Head and neck
- Hepatobiliary
- Refractory Hodgkin lymphoma
- Sarcoma
- Testicular germ cell tumor
| Gemcitabine mimics cytosine and is transported into cells and phosphorylated to its triphosphate form to inhibit DNA synthesis by acting as a competitive inhibitor of DNA polymerase and by inhibition of RNR (targets M1 subunit)
Is usually given at 1,000 mg/m2 IV over 30 minutes
Is activated intracellularly by deoxycytidine kinase (DCK); may be given at fixed dose rate (FDR), e.g., 10 mg/m2/min to avoid DCK saturation | - Intravenous (IV) administration. Can also be administered via intravesical instillation
- Adverse events include:
- myelosuppression (mainly neutropenia)
- edema
- fever
- hepatotoxicity (primarily elevated transaminases but can elevate bilirubin too)
- flu-like syndrome, including chills, cough, headache, rhinitis, myalgia, and fatigue
- erythematous pruritic maculopapular rash
- Rare adverse event: pneumonitis, hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)/thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
|




