Mechanism of methotrexate (MTX) breakdown via glucarpidase.
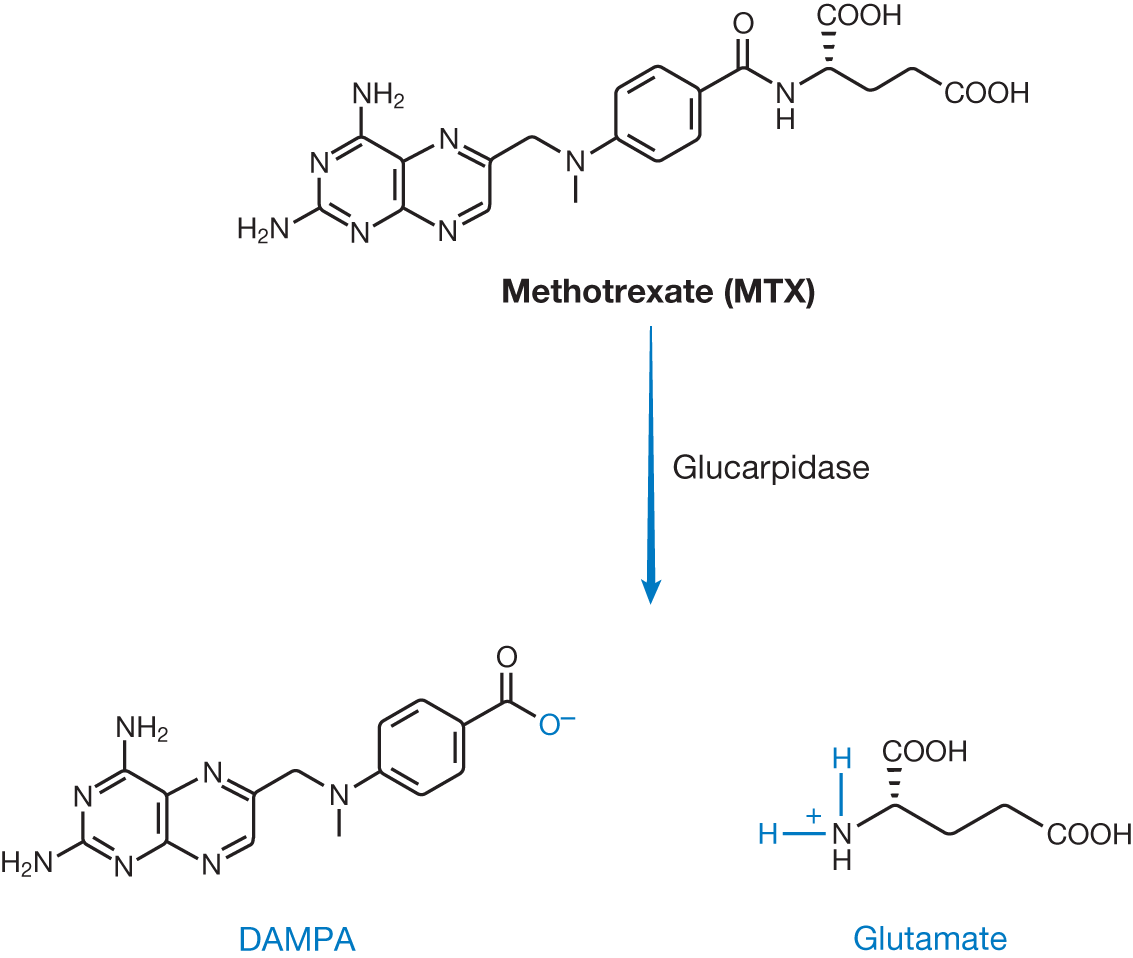
In circumstances of kidney injury that occur despite appropriate precautions of hydration and urine alkalization, leucovorin rescue will NOT be of benefit, because leucovorin acts intracellularly and renal toxicity is a mechanism of extracellular methotrexate crystallization within the renal tubules. Rescue can be achieved with glucarpidase, a recombinant carboxypeptidase that enzymatically and rapidly cleaves MTX to form the amino acid glutamate and soluble 2,4-diamino-N10-methylpteroic acid (DAMPA). It is important to note that depending on the MTX assay being used to monitor blood levels, DAMPA may provide a false-positive until eliminated from the body. As glucarpidase will also act on extracellular leucovorin, leucovorin should not be administered within 2 hours before or after glucarpidase administration.