DESCRIPTION 
- Orthostatic hypotension is defined as a decrease in BP of >20 mm Hg systolic, or 10 mm Hg diastolic, accompanied by symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion, that occurs within 2–5 min of standing.
- Synonym(s): Postural hypotension.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Prevalence 
- Prevalence increases with age: 6.6% among individuals 25–74, 20% in subjects >65 yr, 30% among subjects >75.
- >50% of nursing home residents have orthostatic hypotension.
RISK FACTORS 
- Age >65
- Systolic HTN
- Carotid stenosis >50%
- Use of oral hypoglycemic agents
Genetics 
- Most cases are not caused by hereditary illness.
- Heritable causes are rare and include:
- Autosomal-dominant familial amyloid neuropathy
- Porphyria
- Autosomal-recessive familial dysautonomia-Riley-Day syndrome
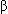 -Hydroxylase deficiency
-Hydroxylase deficiency- Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 
- The effect of gravity will shift 400–800 mL of blood from the thoracic to the abdominal cavity upon standing in the normal individual, leading to a decline in the venous return to the heart.
- This leads to a 40% reduction in the stroke volume, which then leads to a fall in the systemic BP.
- This activates the cardiopulmonary, carotid sinus, and aortic arch baroreceptors, leading to sympathetic activation and parasympathetic inactivation. The result is an increase in heart rate (10–15 bpm) and peripheral resistance, increasing the diastolic BP by 10 mm Hg with no change in the systolic BP.
- This is followed by neurohormonal changes, with activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and vasopressin.
- Normal aging leads to a reduction in the baroreflex sensitivity, resulting in a blunted response to upright posture.
- Normal aging increases the stiffness of the heart, resulting in impaired cardiac relaxation. Any condition that decreases cardiac filling (like reduction of venous return during upright posture) will therefore lead to an exaggerated reduction in the cardiac output.
ETIOLOGY 
Postural hypotension results from 2 mechanisms: Relative volume depletion or autonomic failure.
COMMONLY ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS 
- Nonneurogenic causes:
- Hypovolemia (blood loss or dehydration)
- Vasodilation (vigorous exercise or excessive heat)
- Neurogenic causes:
- Drugs:
- CNS–mediated (methyldopa, reserpine, clonidine, barbiturates, amphetamine, anesthetics, minoxidil)
- Peripheral nervous system–mediated (
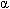 -blockers,
-blockers, 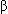 -blockers)
-blockers) - Combination central and peripheral (tricyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines, levodopa)
- Autonomic neuropathy (alcohol, vincas)
- Vascular dilatation (nitrates, hydralazine, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-II antagonists, potassium channel blockers, calcium antagonists, endothelin antagonists)
- Metabolic diseases (DM, chronic renal failure, chronic liver disease, vitamin B12 deficiency, alcohol-induced, Fabry, Tangiers, porphyria)
- Inflammatory (Guillain-Barré, transverse myelitis)
- Infections (syphilis, HIV, Chagas, botulism, tetanus, herpes zoster)
- Neoplasia (brain tumors, especially 3rd ventricle or posterior fossa, paraneoplastic)
- Connective tissue disease (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Surgery/trauma (sympathectomy, spinal cord transection)
- Neurally mediated (vasovagal, carotid sinus hypersensitivity, micturition syncope, cough syncope, swallow syncope)
- Primary chronic autonomic failure syndromes:
- Multiple system atrophy (MSA)
- Parkinson disease
- Multiple cerebral infarcts
- Secondary neuropathies (congenital growth factor deficiency, familial amyloid neuropathy, Riley-Day syndrome, dopamine
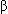 -hydroxylase deficiency, aromatic-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency)
-hydroxylase deficiency, aromatic-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency) - Primary acute and subacute dysautonomias
Outline
History 
- A detailed history is very important in making the diagnosis.
- Dizziness, visual disturbances, loss of consciousness/syncope, impaired cognition, seizures (cerebral hypoperfusion)
- Classically associated with head-up positional change
- May be asymptomatic, especially if longstanding
- Syncope:
- Abrupt drop-attack: No warning symptoms
- Gradual loss of consciousness: More common
- Fatigue, lethargy
- Falls (especially in the elderly)
- Lower back/buttock pain or suboccipital/paracervical "coat-hanger" pain (muscle hypoperfusion)
- Angina pectoris
- Oliguria
- Orthostatic hypotension is more common in the morning, after meals or alcohol.
- Contributory medications
- History of recent volume loss or dehydration
- Symptoms of parkinsonism, diabetes, or peripheral neuropathy
Physical Exam 
- Measurement of BP and heart rate: Supine (after resting for 5 min), sitting and standing up (after 1–3 min)
- Careful neurological evaluation for signs of parkinsonism, neuropathy, CHF, dehydration
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION 
- A hypotensive response can be delayed: Prolonged standing or a tilt test may be required to elicit signs and symptoms.
- BP decreases after 3 min in the upright position (usually standing, but may occur with in severely orthostatic individuals):
- Non-neurogenic causes produce tachycardia and sometimes sweating.
- Neurogenic causes include a decrease in BP without tachycardia.
Lab 
General electrolytes, glucose, hematocrit, creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen may help identify contributory causes. Plasma catecholamine measurements in supine and upright positions may help in differentiating certain neurologic conditions.
Imaging 
May be useful to determine specific suspected cause:
- MRI (for brain or spinal cord lesions)
- Genetic testing (for familial amyloid neuropathy)
- Sural nerve biopsy for peripheral neuropathy
Diagnostic Procedures/Surgery 
- Tilt-table measurement of BP in supine and upright position
- Ambulatory BP monitoring
- Exercise testing or carotid massage may be helpful in determining cause
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 
- Drug effect, especially antidepressant drugs
- Lewy body syndromes
- Multiple system atrophy
- Diabetic, autoimmune, or amyloid neuropathy
- Paraneoplastic autonomic failure
- Reflex syncope
- Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS):
- More common in young patients
- Symptoms occur with tachycardia but without drop in BP.
Outline
ADDITIONAL TREATMENT
General Measures 
- Correction of non-neurogenic causes (eg, hypovolemia) is curative.
- For neurogenic orthostatic hypotension, discontinue medications that may be causative.
- Avoid sudden head-up position changes, prolonged recumbency, straining during micturition/defecation, and vasodilatory stimuli (eg, alcohol, large meals, overheating, vigorous exercise).
- Head-up tilt (15–30 degrees) at night may increase BP by activation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
- Ensure adequate fluid and salt intake.
- Identify body positions (leg-crossing, stooping, squatting) that may attenuate hypotension.
- Elastic stockings and abdominal binders may help, but often are not acceptable to patients.
- Water ingestion 30 min before getting out of bed and before meals.
- Avoid water ingestion before sleep.
- Frequent small meals (avoid large meals).
SURGERY 
Cardiac pacemakers are rarely indicated, except in some forms of neurally mediated syncope, such as carotid hypersensitivity.
Outline
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS
Patient Monitoring 
- Ambulatory BP monitoring may be helpful for evaluation of therapeutic measures.
- Dissociation between BP and symptoms may occur.
- Patients should be taught to record their BP in different positions and at different times of the day to review with their care provider.
DIET 
- Increased salt and water intake may improve the reduction in central blood volume associated with autonomic insufficiency.
- Postprandial BP declines less in patients who drink water during meals.
- Caffeine in the morning is probably helpful to most patients.
PATIENT EDUCATION 
- Education and cooperation are essential for nonpharmacologic preventative measures, as detailed in General Measures.
- Change position in slow stages from lying to sitting to standing.
- Avoiding straining and coughing.
- Avoid exertion in hot weather.
- Raising the head of the bed 10–20 degrees may decrease nocturnal diuresis and supine HTN.
- Elastic stockings that encompass legs and abdomen may be helpful, but are often poorly tolerated.
- Exercise may diminish symptoms as conditioning improves.
PROGNOSIS 
- Prognosis is determined by underlying cause rather than the postural hypotension itself.
- In non-neurogenic orthostatic hypotension, treatment of cause and/or reversal of the underlying deficit may be curative.
- Orthostatic hypotension has been shown to be associated with increased mortality.
COMPLICATIONS 
Goals of therapy for chronic orthostatic hypotension are to ensure mobility and prevent falls that can cause substantial morbidity and mortality.
Outline
CODES
ICD9 
458.0 Orthostatic hypotension
SNOMED 
28651003 orthostatic hypotension (disorder)
CLINICAL PEARLS 
- Careful review of all medications, prescription and OTC, may reveal culprit or contributors.
- Patients with orthostatic hypotension often have significant supine HTN, which can be the cause of considerable end-organ damage and may be overlooked.
Outline
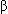 -Hydroxylase deficiency
-Hydroxylase deficiency
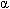 -blockers,
-blockers, 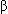 -blockers)
-blockers)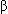 -hydroxylase deficiency, aromatic-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency)
-hydroxylase deficiency, aromatic-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency)