DESCRIPTION 
- Cardiomyopathy (CM) is defined as disease of the heart muscle with histologic or morphologic myocardial abnormality resulting in myocardial dysfunction. The LV is usually affected, or there may be biventricular involvement.
- Primary CMs are of unknown origin; secondary CMs occur when disease is a result of another known systemic disorder.
- The World Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiologists (WHO/ISFC) adopted this empiric division in 1995.
- The 4 main types of primary CM are classified morphologically:
- Dilated: LV dilation; poor systolic function; disproportionately thin free wall and septal thickness; loss of myocytes, fibrosis
- Hypertrophic: LV and/or RV hypertrophy, concentric or asymmetric, involving septum; LV volume normal or reduced; normal systolic, abnormal diastolic function; massive myocyte hypertrophy and fiber disarray with increased connective tissue
- Restrictive: Restrictive filling, low diastolic volume of either ventricle; near-normal systolic function and wall thickness; fibrosis of myocardium, endocardial rigidity
- Arrhythmogenic RV cardiomyopathy (ARVC): Fibrofatty infiltration of RV with associated dilation and systolic dysfunction
- Several as yet unclassified cardiomyopathies may exhibit physiological and pathological overlap with the broad WHO/ISFC categories above:
- Noncompaction CM: Abnormal compaction of the ventricular endocardium resulting in prominent trabeculations, may have systolic and/or diastolic dysfunction
- Endocardial fibroelastosis (EFE): Excessive endocardial thickening secondary to proliferation of fibrous and elastic fibers, primary (genetic disorder) or secondary (congenital heart disease), usually diastolic dysfunction, may progress to dilation and systolic dysfunction.
EPIDEMIOLOGY 
Estimates of incidence of CM vary widely according to type and age group. Overall incidence from 1 current report is 1.13/100,000 children. Variability reported according to age, race, sex, and type of disease.
Incidence 
- Dilated CM accounts for ~51% of all cardiomyopathies seen in childhood:
- Finnish Study: 0.65/100,000 aged <20 yr
- Pediatric Cardiomyopathy Registry: 0.57/100,000 children with infant cases much higher at 4.4/100,000. They found a higher incidence in boys and in black race.
- Hypertrophic CM: ~42% of pediatric CM
- Australian Study: 0.32/100,000
- Pediatric Cardiomyopathy Registry: 0.47/100,000 children; infant incidence higher at 3.2/100,000, and a higher incidence in boys and in black race.
- Restrictive CM: Rare 2–5% of pediatric CM; includes contracted form of EFE
- ARVC: Rare <1% of pediatric CM; typically seen in young adolescent boys:
- Italian Study: 1/5,000 over all age groups
RISK FACTORS 
None for idiopathic; some risk factors for specific etiologies are listed in subsequent text
Genetics 
Overall, 30% of cardiomyopathies may be genetic in origin:
- Dilated CM is 20–30% genetic in origin (mainly autosomal dominant); 9–39% associated with neuromuscular disorders and 16–27% postmyocarditis, depending on the study.
- Hypertrophic CM is 50–60% genetic, with 35% of these familial (autosomal dominant) and 26% inborn errors of metabolism (autosomal recessive).
- Restrictive CM is <10% genetic with the majority being autosomal dominant.
- ARVC is 30–50% genetic with the majority being autosomal dominant inheritance.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 
- Dilated CM is a disease affecting the cytoskeleton and sarcolemma of the myocardium that causes a disruption of systolic function, thought to be a failure of "force transmission," whether on a genetic or secondary basis.
- Hypertrophic CM (also some restrictive CM) is a disease of the sarcomeric proteins, which are responsible for impaired "force generation," and contraction of the muscle.
- ARVC is a disease affecting the cell junction of the myocardium, leading to abnormal strength of the cardiac tissue and early apoptosis, leading to fatty infiltration.
ETIOLOGY 
- Cardiomyopathies are a result of damage to the heart muscle.
- Dilated CM may be idiopathic (unknown etiology), familial/genetic, viral and/or autoimmune, alcoholic/toxic, or associated with other disease:
- 15 genetic loci have been identified for autosomal dominant dilated CM
- Hypertrophic CM may be sporadic, associated with syndromes or more commonly familial, with autosomal-dominant pattern and wide variability of penetrance:
- 60% of families have >1 case.
- 16 genes have so far been associated with familial hypertrophic CM
- Restrictive CM may be idiopathic, familial, or associated with infiltrative disease (amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, glycogen, and hypereosinophilia):
- Troponin I and desmin gene mutations are associated in inherited disease
- ARVC may be sporadic or familial (autosomal dominant) and in 2/3 of cases may have associated myocarditis
COMMONLY ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS 
- Primary CMs, by definition, have no associated conditions. In the specific CMs, >100 associated diseases have been identified:
- Noonan syndrome is associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Barth syndrome is associated with X-linked dilated CM
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy is associated with dilated CM
Outline
Signs and symptoms:
- Symptoms depend on morphologic type of CM and degree of impairment of ventricular muscle and function.
- Dilated CM:
- Initial symptoms range from exercise intolerance to overt CHF as consequence of poor systolic function:
- Respiratory distress, chronic cough, frequent "upper respiratory infections," shortness of breath
- Palpitations/arrhythmias, tachycardia
- Easy fatigability (during feeding with infants)
- Abdominal complaints, pain, nausea, vomiting
- Failure to thrive, growth failure
- Hypertrophic CM:
- Termed "the great masquerader," because signs and symptoms usually result in a false diagnosis of other diseases. Symptoms vary in intensity, depending on the extent and distribution of the hypertrophy. They result from high filling pressures (diastolic dysfunction), low cardiac output from LV outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction, or angina. Obstruction may occur at rest or with provocation:
- Increased fatigability, exercise intolerance
- Cough, breathlessness, "asthma"
- Chest pain
- Syncope or dizziness
- Palpitations: Atrial or ventricular arrhythmias
- Sudden death
- Restrictive CM:
- Presentation varies with age and degree of diastolic impairment:
- In newborn, CHF common with respiratory distress and low output
- Pronounced growth retardation in young children
- Abdominal pain or GI complaints
- Dyspnea on exertion, dry cough, and "asthma" in older children.
- Symptoms may progress faster than other forms of cardiomyopathy.
- Hepatomegaly, ascites, and peripheral edema in older children with more chronic course.
- Palpitations: Atrial arrhythmias, predominantly fibrillation and flutter
- Thromboembolism secondary to atrial thrombus.
- ARVC:
- Common presentation is syncope from ventricular tachyarrhythmias;
- Palpitations, dizziness, aborted sudden death from arrhythmias
- Hepatomegaly, ascites, peripheral edema from isolated right heart failure
- Left heart failure may be seen, but RV failure always predominates
History 
A careful attention to history for symptoms and family screening is important:
- Familial cases often silent with variable expression of disease (all types of CM) until index case is diagnosed
Physical Exam 
- Dilated CM:
- Signs of CHF: Tachycardia, tachypnea, rales, gallop rhythm, hepatomegaly, diminished perfusion, edema
- Murmur of mitral incompetence may be heard with severe LV dilatation
- Hypertrophic CM: The murmur and exam are related to hemodynamic state:
- Outflow obstruction: Double or triple apical LV impulse and medium pitch systolic ejection murmur (increases with Valsalva maneuver)
- Nonobstructive form: Only nonspecific ejection murmur
- Restrictive CM: Depending on degree of diastolic dysfunction, may or may not have significant physical findings:
- 3rd heart sound, prominent apical impulse, increased jugular venous pressure
- Hepatomegaly, ascites, edema
- Rales, wheezing
- ARVC: Depending on degree of systolic dysfunction may have:
- Signs of CHF: Tachycardia, tachypnea, rales, gallop rhythm, hepatomegaly, diminished perfusion, edema
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION 
- EKG: Varying patterns of LV hypertrophy with nonspecific left precordial inversion or flattening of T waves and sometimes deep Q waves.
- Abnormalities specific to each form:
- Dilated: Ventricular, atrial arrhythmias; in EFE very tall QRS voltage present in all precordial and limb leads
- Hypertrophic: 90% abnormal ECG with a wide variety of patterns; infants often have paradoxic RV hypertrophy; cannot discriminate LVOT obstruction or risk for sudden death by ECG; atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia
- Restrictive: Biatrial enlargement, RV enlargement in infants, atrial arrhythmias or progressive heart block
- ARVC:
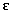 -Waves (electrical potentials of small amplitude at end of QRS complex) are highly specific in 1/3 of cases; right bundle branch block (RBBB) pattern at baseline, left bundle branch block type ventricular tachycardia.
-Waves (electrical potentials of small amplitude at end of QRS complex) are highly specific in 1/3 of cases; right bundle branch block (RBBB) pattern at baseline, left bundle branch block type ventricular tachycardia.
Lab 
Blood and urine tests can help to determine etiology in some cases, especially if CM is secondary to other diseases:
- Metabolic causes such as carnitine deficiency, thyroid disorders, or fatty acid oxidation defects
- Genetic testing should be performed to rule out known causes.
- Exposure to viruses that may have caused myocarditis and/or ongoing inflammation or autoimmune causes of CM.
Imaging 
- Evaluations establish diagnosis and monitor treatment effectiveness.
- CXR: Enlarged heart:
- Dilated CM: Larger, more globular shape, pulmonary edema or congestion, left atrium dilated
- Hypertrophic CM: Cardiomegaly greater in infants than older children, unless end-stage
- Restrictive CM: Biatrial dilatation, pulmonary venous congestion pattern, ventricular enlargement not prominent
- ARVC: Possible RV enlargement
- Echo: Provides definitive diagnosis of four morphologic types, rules out other abnormalities:
- Dilated CM: Thin-walled, globular LV, low fractional shortening, mitral insufficiency and/or mural thrombi in late stages, both ventricles can be affected
- Hypertrophic CM: Very thick septum, free wall, near obliteration of LV cavity, normal to hyperdynamic function, systolic anterior motion of mitral leaflet, and/or LVOT obstruction with measurable Doppler gradient. In some cases may only have concentric hypertrophy. Classic IHSS features as seen in adults are often not present in children.
- Restrictive CM: Massive biatrial enlargement, normal to small-sized somewhat hypertrophied ventricles, normal systolic function with abnormal diastolic function
- ARVC: RV dilation and systolic dysfunction with no or mild LV impairment, localized RV aneurysm
- Other CM: Noncompaction is easily seen with 2:1 of noncompacted to compacted endocardium, may be seen at apex or diffuse.
- Angiography: Only indicated if unable to visualize coronary arteries by echo or to rule out discrete aortic obstruction
- MRI:
- Useful to rule out constrictive pericarditis from restrictive cardiomyopathy, and diagnose EFE
- ARVC: Better evaluation of RV dilation, dysfunction, aneurysms and may show fatty infiltration.
Diagnostic Procedures/Surgery 
- Cardiac catheterization:
- Dilated CM: Evaluate for myocarditis by endomyocardial biopsy, evaluate hemodynamic efficacy of medical therapy and need for transplantation.
- Hypertrophic CM: Evaluation for arrhythmias and possible surgical relief of obstruction.
- Restrictive CM: Rule out constrictive pericarditis (dip and plateau pressure tracing present in both diseases, LV end-diastolic pressure > RV end-diastolic pressure favors restrictive CM). Pulmonary HTN with rapidly increasing resistance is seen frequently and earlier in restrictive types but not in hypertrophic type.
- ARVC: Evaluate for arrhythmias; angiography has been used in past as gold standard diagnostic test, now usually MRI.
- Skeletal muscle biopsy sometimes is needed to diagnose myopathies associated with systemic or neuromuscular disorders.
Pathological Findings 
- Dilated CM from all causes:
- Loss of myocytes with some hypertrophy of remaining myocytes and fibrosis, myocardium generally thinned
- Hypertrophic CM:
- Massive myocyte hypertrophy and fiber disarray with increased connective tissue and thickness of the myocardium
- Restrictive CM:
- May have interstitial fibrosis and some myocyte disarray along with hypertrophy; endocardial thickening can also be seen in affected ventricles and atria
- In secondary restrictive cases, abnormal deposits can be seen such as amyloid and iron.
- ARVC:
- Fibrofatty replacement with thinning of myocardium.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 
- The differential diagnosis of idiopathic CM is one of exclusion.
- Diagnostic focus should center on establishing an etiology that might be curable:
- Myocarditis
- Rule out anomalous coronary and coarctation of the aorta in dilated CM
- Other examples of treatable causes of dilated CM are carnitine deficiency, arrhythmia, toxic reactions, and inflammatory diseases.
- A treatable cause of hypertrophic CM is subaortic membrane
- Constrictive pericarditis must be ruled out in cases of restrictive CM.
- Usually there is no difficulty diagnostically in distinguishing dilated CM from other forms of CM.
Outline
Presentation can vary from asymptomatic, to mild CHF, to shock. Treatment and medications will vary accordingly from outpatient to ICU.
First Line 
- Dilated CM:
- CHF treatment should be tailored and maximized. Some of these agents may be needed in other types of CM in later stages.
- Digoxin
- ACE inhibitors
- Diuretics such as furosemide or thiazides. Fluid restriction may be required for severe heart failure and hyponatremia.
- Spironolactone may be added to maintain potassium levels (caution when adding to ACE inhibitor).
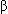 -Adrenergic blockers may result in significant improvement, but should only be administered cautiously, under direct care of experienced cardiologist, and never in decompensated CHF.
-Adrenergic blockers may result in significant improvement, but should only be administered cautiously, under direct care of experienced cardiologist, and never in decompensated CHF.- If outpatient management is unsuccessful, or if patient is unstable on presentation, IV inotropic agents and vasodilators may be necessary for stabilization; in extreme cases, ventilatory support or LV assist devices may be needed.
- Arrhythmia management: Isolated or even frequent premature ventricular beats do not warrant the addition of an antiarrhythmic unless:
- Episodes of ventricular tachycardia with syncope are featured: Amiodarone
- Implantable defibrillator may be a better option for malignant rhythms
- Hypertrophic CM:
- Treatment usually is focused on minimizing outflow obstruction, myocardial relaxation, and arrhythmia control (see preceding).
- Calcium channel blockers may alleviate symptoms and questionably prevent progression of disease.
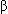 -Blocker therapy may decrease ectopic beats while controlling heart rate and LV compliance.
-Blocker therapy may decrease ectopic beats while controlling heart rate and LV compliance.- If CHF occurs, cardiotonics may be necessary but may increase chance of ischemia. Caution is needed when using diuretics in hypertrophic or restrictive CM where cardiac output is dependent on preload.
- Restrictive CM:
- No specific medications. Children most often need anticongestive measures that can share the same danger as with hypertrophic patients. Rarely atrial arrhythmias may arise and require treatment.
- ARVC:
- Arrhythmia management includes sotalol, verapamil, and amiodarone.
Second Line 
ARBs can be substituted when ACE inhibitors are not tolerated.
Outline
ADDITIONAL TREATMENT
General Measures 
- Medical management involves control of CHF and arrhythmias and potential prevention of progression of disease. In asymptomatic patients continued re-evaluation is warranted.
- A tailored cardiotonic regimen for patients with CHF is optimal.
- Use of medications to modulate the neuroendocrine system in asymptomatic patients may prevent progression of disease.
- To prevent thromboembolism, warfarin or Lovenox anticoagulation is advised if atrial fibrillation, ejection fraction <20%, and/or mural thrombus is present. Aspirin is adequate if dysfunction not severe.
- Endocarditis prophylaxis is only necessary with concomitant valvular abnormality.
- Influenza and pneumococcal vaccines are advisable with significant cardiovascular compromise, and respiratory syncytial viral prophylaxis in infants <2 yr.
Referral 
A new diagnosis of CM warrants evaluation for etiology and management, which may include:
- Pediatric heart failure/transplant specialists
- Geneticist
- Neurologist specializing in neuromuscular disorders
- Pediatric electrophysiologist
SURGERY 
- Hypertrophic CM: Excision of muscular LVOT or RV outflow tract obstruction can relieve symptoms.
- Hypertrophic CM: Resolution of symptoms may occur with release of coronary stenosis by myocardial bridging.
- Implantable defibrillators help prevent outpatient sudden death when ventricular arrhythmias are significant in hypertrophic CM and ARVC.
- When maximal medical therapy fails, cardiac transplantation should be considered.
- The use of mitral valvuloplasty or replacement and/or ventricular reduction therapy in dilated CM has not been proven efficacious.
IN-PATIENT CONSIDERATIONS
Admission Criteria 
- Children can present with mild to severe CHF or shock at time of diagnosis with dilated CM:
- With significant CHF symptoms patients might initially need to be placed on bed rest with supplemental oxygen and fluid restriction until stabilized.
- Patients in shock should be stabilized in the intensive care setting and transitioned to PO medicines and a nonintensive setting for teaching.
- After stabilization and discharge, repeat admissions usually are for acute pulmonary edema or transient low output or progression of disease.
- Patients with hypertrophic CM and ARVC usually do not require admission except for life-threatening arrhythmia or if end stage:
- Patients who have syncope should be admitted for observation for acute arrhythmia or ischemia.
- Restrictive patients can have episodic increase in CHF symptoms, and with rising pulmonary vascular resistance index will need transplantation sooner than dilated patients to avoid need for concomitant lung transplantation. Symptoms may progress rapidly in this form of cardiomyopathy.
Discharge Criteria 
Patients whose CHF is stabilized and are able to take their medications and tolerate activities of daily living can be discharged to be followed as an outpatient:
- In infants, the ability to take and/or tolerate feeding is critical to their CHF management.
Outline
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS 
The frequency of follow-up is dictated not only by type of CM but by severity of symptoms. Since these diseases progress with time, follow-up by a qualified pediatric cardiologist is essential.
Patient Monitoring 
- Close outpatient follow-up of all patients with CM is necessary to detect progression of disease and to tailor medications.
- Frequency of visits will depend on cardiac disability and instability. Progress can be evaluated by periodic:
- Exercise testing: To determine VO2max in dilated patients, and level of inducible ischemia in hypertrophic CM
- Holter monitoring: To detect malignant arrhythmias or progressive heart block
- Electrolyte profile should be closely followed with use of digoxin and diuretics. Serum sodium and renal function can be a marker for degree of heart failure.
- Use of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) measurements may help in following progression of CHF and predicting adverse cardiovascular events.
- Cardiac catheterization: Pretransplantation hemodynamic testing and progression of pulmonary vascular resistance index (PVRI)
DIET 
- Children with CM usually have trouble taking in enough calories secondary to the disease or CHF symptoms and often have a higher caloric requirement:
- Higher-calorie diet or supplements for children with failure to thrive
- Infants may need tube feeding; older children small frequent meals.
- Low-salt foods when symptomatic CHF or fluid retention
- Foods high in potassium and magnesium are good to help maintain adequate levels when on diuretics.
- Certain metabolic cardiomyopathies may require special diets to prevent disease progression.
PATIENT EDUCATION 
- Activity:
- Hypertrophic CM and ARVC: Strenuous physical exercise and stress should be avoided, and more sedentary recreation advocated.
- Dilated and restrictive CM: Recommendations for activity according to the degree of ventricular dysfunction and symptomatology.
- Patients with CM and/or CHF and their family should be educated about:
- Importance of low-salt diet and fluid restriction when necessary
- Adequate rest, but graded regular exercise important (cardiac rehabilitation based on the severity of compromise) in dilated CM.
- Patients with hypertrophic CM must not pursue vigorous exercise, or competitive sports.
- Importance of routine follow-up and compliance with medications.
- Signs and symptoms of disease progression and arrhythmias.
- Numerous websites and support organizations for patients with heart failure and CM. Many American Heart Association (AHA) sites exist, but most geared to older adolescents or adults:
PROGNOSIS 
Prognosis varies with the type of CM:
- Dilated CM:
- Course is highly variable, with some children surviving many years but a significant number lost in the 1st yr after diagnosis.
- A recent study estimated 1-year freedom from death or transplantation after diagnosis of DCM, 69%; 5-year, 54%; 10-yr, 46%.
- Patients presenting in CHF had a 4-fold increase in hazard of death or need for transplantation in the 1st yr.
- Symptoms of CHF despite therapy are a poor prognostic sign.
- LV ejection fraction most often is not predictive of clinical course.
- Elevated LV end-diastolic pressure >25 mm Hg: Mortality 46% at 1 yr, 68% at 5 yr
- Low serum sodium correlated with poor outcome
- Use of cardiac transplantation has improved survival with dilated CM to 87 % at 1 yr and 77% at 5 yr.
- Hypertrophic CM:
- Course depends on age at presentation.
- Infant survival dismal with CHF; transplantation should be considered
- Most diagnosed after age 12 yr are stable for many years.
- 3–6% annual mortality rate; 5-yr survival, 80%
- Progressive disease, especially during rapid somatic growth
- Sudden death during exercise most common in adolescents.
- No predictive variables for sudden death in children, but sudden death of 1st-degree relative can be an important prognostic sign
- Extreme LV hypertrophy and inappropriate BP response to exercise may be associated with end-stage CHF
- Late dilation may occur with CHF
- If late CHF or unmanageable symptoms develop, transplantation is indicated.
- Restrictive CM:
- Rare, but course is accelerated, with most deaths occurring in young childhood, either sudden or from advancing CHF. May have a period of well-being after initial CHF symptoms, when pulmonary resistance increases. Transplantation should be considered early.
- ARVC:
- Sudden death is major cause of death in ARVC, especially in young athletes. No predictive variables for sudden death. CHF symptoms may not develop until adulthood. If late CHF or malignant arrhythmias develop, transplantation is indicated.
Pregnancy Considerations 
- Risk for pregnancy depends on degree of ventricular dysfunction and/or heart failure.
- Symptomatic patients with dilated CM and all patients with hypertrophic CM are at increased risk for mortality and for cardiovascular decompensation during pregnancy.
COMPLICATIONS 
Complications relate to the progression of heart failure and its effects on other organ systems, either from low output or chronic congestion:
- Cirrhosis, renal dysfunction, cachexia, recurrent pulmonary infections, pulmonary HTN, and decreased mentation may all occur with severe chronic CHF.
- Other circulatory complications such as stroke and peripheral vascular abnormalities can also result.
Outline

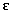 -Waves (electrical potentials of small amplitude at end of QRS complex) are highly specific in 1/3 of cases; right bundle branch block (RBBB) pattern at baseline, left bundle branch block type ventricular tachycardia.
-Waves (electrical potentials of small amplitude at end of QRS complex) are highly specific in 1/3 of cases; right bundle branch block (RBBB) pattern at baseline, left bundle branch block type ventricular tachycardia.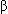 -Adrenergic blockers may result in significant improvement, but should only be administered cautiously, under direct care of experienced cardiologist, and never in decompensated CHF.
-Adrenergic blockers may result in significant improvement, but should only be administered cautiously, under direct care of experienced cardiologist, and never in decompensated CHF.