DESCRIPTION 
- Atrial premature beats or complexes (APCs) are early atrial systoles identified on the EKG by early P waves.
- The contour of the P wave may resemble sinus P waves, but it is usually different.
- APCs mimic sinus P waves when they arise near the sinus node
- When P waves occur very early, atrioventricular (AV) conduction may remain refractory, such that the impulse is not propagated to the ventricles (blocked APC).
- Sometimes the P wave of an APC is difficult to identify because it falls in the T wave of the preceding QRS complex.
- Synonym(s): Atrial premature complexes; Atrial premature contractions
Pregnancy Considerations 
- Pregnancy may exacerbate frequency of APCs.
- Changes in intravascular volume and subsequent atrial wall stress may trigger stretch-induced atrial arrhythmias.
EPIDEMIOLOGY 
APCs increase with aging; in the elderly, APCs are ubiquitous.
RISK FACTORS 
Structural heart disease with abnormalities of atrial structure or physiology, such as infiltrative diseases (amyloid), RV or LV failure, mitral or tricuspid insufficiency, following cardiac surgery, pericarditis
ETIOLOGY 
- Often, APCs have no particular cause and are a function of aging myocardium.
- During times of stress and sympathetic stimulation
- Hyperthyroidism
- With MI in >50% of patients
- In association with elevated atrial pressure and wall stress, for example LV failure or cor pulmonale
- Alcohol, tobacco, and caffeine consumption
- Drug toxicity, for example, digitalis toxicity
Outline
Signs and symptoms:
- Usually none, but occasionally can be felt as palpitations
- They may presage sustained supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and atrial flutter.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION 
- EKG
- Event recorder; especially useful to correlate symptoms with PACs
- Holter monitor, useful to correlate symptoms and assess frequency of PACs
- Telemetry in hospital
Lab 
- None per se, except to test for hyperthyroidism
- ESR if myocarditis or pericarditis suspected
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 
- Junctional premature beats
- Wandering atrial pacemaker
Outline
First Line 
- If palpitations are a major complaint,
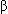 -blockade may be helpful.
-blockade may be helpful. 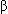 -Blockers:
-Blockers:
- May decrease catecholamine stimulus, vigor of post-APC ventricular contraction, or timing of ventricular contraction, thereby improving symptoms
- In otherwise healthy patients, adverse drug effects may be worse than symptoms resulting from the arrhythmia.
- Calcium channel blockers
Second Line 
In highly symptomatic patients not responding to previously described medical therapy, antiarrhythmic drugs (class 1C if no structural heart disease, or class 3) can be tried, either alone or in combination with 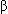 -blockers.
-blockers.
Outline
ADDITIONAL TREATMENT
General Measures 
Usually no treatment is indicated or required.
SURGERY 
In selected patients, electrophysiologic mapping and catheter ablation of the PAC focus is possible.
IN-PATIENT CONSIDERATIONS
Admission Criteria 
Not applicable; patients are typically not admitted for APCs.
Outline
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS
Patient Monitoring 
- Mostly never needed, follow clinical symptoms
- If monitoring chosen, Holter EKG monitor to quantify daily APC frequency and Event Monitor/Holter EKG to correlate symptoms with rhythm.
PATIENT EDUCATION 
- APCs are common and benign.
- Aggressive treatment with primary antiarrhythmic drugs may lead to morbidity and mortality in excess of that expected from APCs by themselves and can be avoided in most patients.
- Rarely, antiarrhythmic drugs or catheter ablation is required.
- Avoiding caffeine and other precipitating stimuli (alcohol, tobacco) may decrease APC frequency.
- Activity is usually not restricted, but rather encouraged.
PROGNOSIS 
Normal; occasionally APCs may be a harbinger to atrial fibrillation, and may trigger reentrant supraventricular tachycardias.
Outline
CODES
ICD9
427.61 Supraventricular premature beats
SNOMED
287057009 atrial premature complex (disorder)

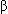 -blockade may be helpful.
-blockade may be helpful.