DESCRIPTION 
Acromegaly is a rare disorder caused by excess production of growth hormone (GH), usually from a pituitary adenoma, that almost always results in cardiomyopathy characterized by biventricular hypertrophy and potential diastolic and systolic heart failure. The cardiomyopathy is due to both direct effects of GH and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), as well as secondary effects from HTN, diabetes, and other comorbid conditions.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Incidence 
The incidence of acromegaly is ~3–4 cases per million persons per year.
Prevalence 
- The prevalence of acromegaly is ~40–60 cases per million persons.
- ~2/3 of patients have echo evidence of cardiomyopathy at time of diagnosis of acromegaly. The lifetime prevalence of cardiomyopathy in acromegaly is ~90%.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 
- GH and IGF-1 (produced by the liver in response to GH) have numerous endocrine, autocrine, and paracrine effects throughout the body, affecting somatic growth, cardiac development and function, and other processes.
- Acromegalic cardiomyopathy is caused by both direct effects of excess serum GH and IGF-I on cardiomyocytes, and secondary effects due to increased systemic HTN, DM, obstructive sleep apnea, and thyroid dysfunction. Elevated levels of triglycerides, apolipoprotein A-1, Apo E, fibrinogen, plasminogen activator inhibitor, and tissue plasminogen activator may also contribute to cardiovascular disease in acromegaly.
- Effects of GH and IGF-1 on cardiomyocytes are not completely understood. They have been shown to augment myocardial contractility, causing increased intracellular calcium concentration and calcium sensitivity. Excess GH can also stimulate cardiac hypertrophy.
- Acromegalic cardiomyopathy progresses through 3 stages if left untreated: Early in the disease process there is increased heart rate and stroke volume, constituting a hyperkinetic syndrome. Cardiac hypertrophy begins very early after exposure to excess GH. In the middle phase, cardiac hypertrophy continues to progress, diastolic dysfunction develops, and systolic dysfunction may also appear. In late phase, systolic heart failure progresses and dilated cardiomyopathy may also develop.
ETIOLOGY 
- GH excess:
- Benign somatotroph (GH-cell) adenomas of the anterior pituitary gland account for >95% of cases of acromegaly.
- Rare etiologies include: Mixed somatotroph (GH-cell) and mammotroph (prolactin-cell) adenoma; plurihormonal adenoma; somatotroph carcinoma; pancreatic islet-cell tumor; lymphoma; iatrogenic cause; and familial syndromes.
- Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) tumors account for <2% of cases of acromegaly.
COMMONLY ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS 
- HTN occurs in 20–40% of cases.
- DM occurs in ~15% of cases.
- Obstructive sleep apnea occurs in >50% of cases.
- Coronary artery disease prevalence does not appear to be elevated.
- Arrhythmias: Atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, sick sinus syndrome, ventricular tachycardia, and bundle branch blocks may be found.
- Thyroid dysfunction is common.
- Skeletal disorders exist in 70% of patients, and account for the most significant functional disability and reduced quality of life.
- Colon cancer risk with acromegaly is twice that of the general population, thought to be the effect of IGF-I on intestinal epithelium.
Outline
History 
- General:
- Diagnosis of acromegaly is often delayed by years due to insidious progression, most often with florid symptoms and signs at time of diagnosis.
- Roughly 40% of diagnoses are made by internists; most others are diagnosed by ophthalmologists for visual disturbances, dental surgeons for bite disorders, gynecologists for menstrual dysfunction/infertility, rheumatologists for osteoarthritis, or sleep specialists for obstructive sleep apnea.
- Heart failure is rarely the presenting feature of acromegaly.
- Cardiovascular:
- Left heart failure: Dyspnea on exertion or at rest; paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea; orthopnea; chest discomfort; decreased exercise tolerance.
- Right heart failure: Peripheral edema; abdominal fullness; nausea; altered mental status; weight gain.
- Arrhythmias: Palpitations; dyspnea; dizziness; syncope.
- Musculoskeletal: Arthralgias; arthritis; carpal tunnel syndrome; acroparesthesia.
- Endocrine: Menstrual abnormalities; galactorrhea; urinary abnormalities due to prostate hypertrophy; decreased libido.
- Neurological: Visual field deficit; headache; central sleep apnea; narcolepsy.
- Pulmonary: Obstructive sleep apnea.
Physical Exam 
- Cardiovascular:
- HTN
- Left heart failure: 3rd heart sound; 4th heart sound; pulmonary rales; LV heave.
- Right heart failure
- Musculoskeletal: Acral enlargement; gigantism (in children or adolescents); prognathism; jaw malocclusion; frontal bossing; macroglossia
- Neurological: Visual field deficits; cranial nerve palsy; proximal myopathy
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION 
- Diagnosis of acromegaly: In the presence of signs and symptoms of acromegaly, a diagnosis is made by demonstration of elevated serum GH and IGF-1 concentrations, plus imaging study showing evidence of pituitary adenoma (in >95% of cases) or other source of excess GH.
- Diagnosis of acromegalic cardiomyopathy: No specific test proves that a patient’s cardiomyopathy is due to acromegaly. Echo, though, typically shows concentric biventricular hypertrophy.
Lab 
- Serum IGF-1 concentration is the 1st test that should be ordered in patients with suspected acromegaly. A normal value rules out acromegaly. An abnormally high value (concentrations are age- and sex-specific) is found with acromegaly and should prompt testing of serum GH concentration and imaging of the pituitary to confirm the diagnosis.
- Serum GH concentration is persistently elevated in acromegaly, with baseline levels 2–10 ng/mL throughout most of the day. However, random GH concentration is not a good test because normal GH release is pulsatile (induced by fasting, exercise, stress, and sleep) ranging from baseline <0.1–1.0 ng/mL up to surge levels of 30 ng/mL, making it difficult to determine whether an elevated value represents a normal surge vs. an abnormal acromegalic baseline.
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with 75 g of glucose followed by measurement of nadir GH concentration after 2 hr is required to confirm diagnosis of acromegaly. Nadir GH Concentration <1 ng/mL (<0.3 ng/mL with high-sensitivity assays) rules out acromegaly.
- NT-proBNP levels may paradoxically be normal in acromegalic cardiomyopathy, and increase after treatment for acromegaly. It has been hypothesized that GH and IGF-1 may suppress secretion of NT-proBNP from cardiomyocytes.
- Other laboratory tests that should be checked: Lipid panel (acromegaly can cause reduced total cholesterol and elevated triglycerides); TSH (thyrotoxicosis may be seen); blood glucose (to assess for DM); parathyroid hormone (may have hyperparathyroidism); reproductive hormones (if menstrual abnormality or infertility exists).
- EKG commonly shows LVH, ST-segment depression, septal Q-waves, T-wave inversion, and/or bundle branch block.
Imaging 
- Pituitary MRI should be performed to determine the source of excess GH. Tumors as small as 2 mm can be detected by MRI. ~75% of somatotroph adenomas are macroadenomas (>10 mm). Of note, 10–20% of the normal population without acromegaly have pituitary microadenomas.
- Chest and abdominal CT scan should be performed to determine source of GH excess if pituitary MRI fails to identify adenoma.
- CXR may show cardiomegaly and/or pulmonary vascular congestion.
- Echo:
- ~2/3 of patients have concentric biventricular hypertrophy at time of diagnosis. Concentric biventricular hypertrophy is the most common echo feature of acromegalic cardiomyopathy, and is an early feature in acromegaly. Eccentric septal hypertrophy may also be seen.
- Tissue Doppler shows diastolic dysfunction.
- Reduced LV ejection fraction and LV dilation may be seen in late stages of disease.
Diagnostic Procedures/Surgery 
Endomyocardial biopsy is not routinely indicated for suspected acromegalic cardiomyopathy, as the histopathological findings are nonspecific.
Pathological Findings 
- Histological findings are nonspecific. Interstitial fibrosis may precede hypertrophy.
- Gross pathology reveals increased LV mass, concentric biventricular wall thickening, or occasionally eccentric ventricular septal thickening.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 
- Consider other causes of ventricular hypertrophy: Hypertensive heart disease; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; amyloidosis; sarcoidosis; hemochromatosis; glycogen storage diseases (eg, Fabry disease); aortic stenosis.
- Other possible coexisting causes of HTN are pheochromocytoma and aldosteronoma.
Outline
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS
Patient Monitoring 
Routine measurement of serum IGF-1 and GH concentrations should be performed to assess effectiveness of treatment. Normal age- and sex-specific IGF-1 concentrations, and GH concentrations <2.5 ng/mL are associated with improvement in cardiac structure and function, as well as restoration of normal life expectancy.
PROGNOSIS 
- Untreated acromegaly results in early mortality, with ~60% of deaths due to cardiovascular disease, 25% due to respiratory disease, and 15% due to cancer.
- Mean age of death was 61±12.8 yr old in 1 case series.
- The major negative determinants of survival are high GH levels, HTN, and heart disease.
- Determinants of improved survival include control of serum GH concentration to <2.5 ng/mL, younger age, shorter disease duration, and absence of HTN.
- Treatment resulting in consistently normal serum IGF-1 concentration may result in normalization of life expectancy to that of nonacromegalic population.
Outline

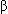 -Adrenergic blockers should probably be used, although there is mixed evidence regarding the role of the adrenergic system in acromegalic cardiomyopathy; both urine catecholamines and plasma
-Adrenergic blockers should probably be used, although there is mixed evidence regarding the role of the adrenergic system in acromegalic cardiomyopathy; both urine catecholamines and plasma