DESCRIPTION 
The 2008 ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of adults with congenital heart disease categorizes patients into those with simple, moderately complex and complex lesions (see Warnes et al.).
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Prevalence 
The prevalence of adults with residual congenital heart defects requiring follow-up is increasing as the number of patients who have had corrective or palliative surgery has increased and survival improves. It is estimated that there are >1,000,000 adults with congenital heart disease in the U.S.
GENERAL PREVENTION 
- Adequate prenatal care
- Fetal ECG for early diagnosis/treatment
- Genetic counseling in those with a family history of congenital heart disease
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 
Varied
ETIOLOGY 
- The cause of most congenital heart disease is unknown; thought to be multifactorial
- An increasing number of cases are known to be genetic.
- 22q11 deletion is associated with conotruncal abnormalities such as interrupted aortic arch, truncus arteriosus, pulmonary atresia with VSD, and tetralogy of Fallot.
- ~2% of cases are environmental (eg, maternal diabetes, infection, and therapeutic or elicit drugs).
- Genetic counseling should be provided for all potential parents with congenital heart disease, both male and female.
Outline
Signs and symptoms vary, depending on type of defect and severity.
History 
- Depending on the underlying lesion, patients may have
 1 of the following:
1 of the following:
- History of murmur in childhood
- History of palliative surgery in early infancy
- History of corrective surgery in early infancy or childhood
- History of arrhythmia
- History of endocarditis
- Cyanosis secondary to uncorrected cardiac defect:
- Effort-induced dyspnea
- Increased cyanosis with exercise
- Effort-induced fatigue
- Cyanosis secondary to pulmonary vascular disease (Eisenmenger syndrome):
- Decrease in intensity of childhood murmur
- Palpable P2, RV heave
- Clubbing of fingers and toes, perioral cyanosis, hypertrophic osteopathy
- Hemoptysis (late)
- Acyanotic:
- Range from asymptomatic to significant limitation of activities of daily living with symptoms at rest secondary to heart failure.
Physical Exam 
- Depends on type of congenital heart disease (CHD)
- Jugular venous pressure:
- Elevated in right-sided heart failure
- Prominent V wave in patients with significant tricuspid regurgitation (TR)
- Carotid artery:
- Prominent upstroke and rapid descent in patients with severe aortic regurgitation (AR)
- Referred murmur from valvar, supravalvar and aortic obstruction; also suprasternal thrill
- Cardiovascular exam:
- Eisenmenger syndrome/primary pulmonary HTN (PPH): RV heave, loud +/- palpable P2, pansystolic murmur of TR
- D-TGV status post atrial redirection: RV heave, loud single 2nd heart sound (S2)
- ASD patients have a fixed split S2, systolic ejection murmur of increased flow across the pulmonary valve, short early diastolic murmur at left sternal border from increased flow across the tricuspid valve, +/- RV heave
- Small VSDs will have a loud pansystolic murmur and often a thrill at the left sternal border.
- Postoperative tetralogy of Fallot patients will often have harsh systolic ejection murmur, and low-pitched diastolic murmur due to significant PR and right ventricular outflow tract turbulence
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION 
- Cardiovascular/pulmonary anatomy:
- Arrhythmia:
- Holter
- Event monitor
- Electrophysiology study
- Functional capacity and cardiac ischemia:
- Standard Bruce protocol exercise stress testing
- Thallium and sestamibi nuclear stress testing
- Cardiopulmonary stress testing
Lab 
- Cyanotic:
- Hemoglobin/hematocrit elevated secondary to elevated erythropoietin levels (hemoglobin 16–23 g/dL, hematocrit 55–80%)
- Platelet count low to markedly reduced
- BUN/creatinine may be elevated.
- Uric acid elevated secondary to inappropriately low renal excretion
- Acyanotic:
- Liver function tests for patients at risk for PLE or liver congestion
- BNP for patients at risk for heart failure
Imaging 
- CXR:
- Cyanotic secondary to pulmonary vascular disease
- Decreased pulmonary blood flow
- Prominent pulmonary arteries at the hilum with rapid tapering
- Enlarged RV silhouette
- Acyanotic:
- Depends on the nature of the underlying lesion
- Transthoracic echo:
- 2D/3D imaging:
- Delineation of segmental anatomy (situs, ventricular looping, great-vessel orientation)
- Evaluation of ventricular systolic function
- Ventricular hypertrophy/dilatation
- Atrial enlargement
- Valve thickness, morphology, prolapse
- Anatomic findings such as membranes, pulmonary artery disease, aortic aneurysm, etc.
- Color flow imaging:
- Following the course of arteries and veins
- Detecting small atrial or ventricular septal defects
- Detecting small aortic-to-pulmonary connections
- Delineating stenotic and regurgitant lesions
- Doppler studies for identification and quantification of:
- Valvular, supravalvular, and subvalvular stenosis
- Valvular regurgitation
- Extracardiac and intracardiac conduit obstructions
- Pulmonary and systemic venous stenoses
- Septal defects
- Surgical shunts
- Diastolic function
- Dp/dt
- Simpson’s estimation of ventricular volume and ejection fraction
- Myocardial performance index
- MRI/MRA:
- Quantitative measure of systemic ventricular volume and ejection fraction
- Evaluation of pulmonary anatomy
- Evaluation of conduit and atrial baffle patency
- Evaluation of pulmonary venous drainage
- Transesophageal echo:
- Evaluate anatomic areas not easily demonstrated by transthoracic echo.
- Monitor therapeutic interventions in the cardiac catheterization laboratory.
- Prior to cardioversion to exclude intracardiac thrombus
- Intraoperative imaging during cardiac surgery
Diagnostic Procedures/Surgery 
- Cardiac catheterization:
- Evaluation of coronary artery atherosclerotic disease
- Evaluate ventricular filling pressures.
- Delineate patterns of collateral blood flow.
- Delineate pulmonary anatomy
- Percutaneous interventions include coil occlusion of aorto-pulmonary collaterals, peripheral pulmonary stenosis, stenting, atrial baffle, stenting ASD/PFO device closure.
Outline
ADDITIONAL TREATMENT
General Measures 
The management of endocarditis prophylaxis has been updated by 2007 ACC/AHA guidelines on endocarditis prevention. Meticulous oral hygiene, skin, and nail care
SURGERY 
Indications for operation in adults with congenital heart disease include:
- Repair of primary congenital heart defect: ASD, aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, Ebstein anomaly, coarctation of the aorta, tetralogy of Fallot, etc.
- Inevitable reoperation: Bioprosthetic heart valve, extracardiac conduit; timing variable.
- Residual defects after repair: Residual mitral valve regurgitation and/or subvalvular aortic stenosis after atrioventricular (AV) canal defect repair
- New/recurrent defects after corrective surgery: Subaortic stenosis recurrence, pulmonary regurgitation after repair of tetralogy of Fallot
- Staged repair of complex defect: Fontan procedure
- Late complications: Infective endocarditis
- Patient with acquired heart disease: Coronary atherosclerotic disease
- Uncorrectable congenital heart disease: Heart or heart/lung transplant
- Insertion of permanent pacemaker and/or defibrillator
- Mapping and ablation of arrhythmias
IN-PATIENT CONSIDERATIONS
Admission Criteria 
- Symptomatic arrhythmia for drug treatment or electrophysiology study (ablation or intracardiac defibrillator placement)
- Exacerbation of CHF
- Surgery or interventional/diagnostic cardiac catheterization
- Endocarditis
- Cerebral abscess or stroke in cyanotic patient
Outline
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS 
- Adult Congenital Heart Disease Center with multidisciplinary approach
- Noninvasive and invasive cardiologists
- Cardiac surgeon with experience in ACHD
- Electrophysiology
- Availability of cardiac MRI, computed tomography (CT)
- High risk OB-GYN
- Hematology
- Nutritionist
- Psychiatry/social work support
Pregnancy Considerations 
- Patients with cyanosis are at high risk of early spontaneous abortion.
- Elevated pulmonary vascular resistance from Eisenmenger syndrome or primary pulmonary HTN is a contraindication to pregnancy.
- Patients with Marfan syndrome and some patients with bicuspid aortic valve and associated with ascending aortic aneurysm are at risk for aortic dissection/rupture.
- Patients with severe obstructive lesions (aortic stenosis, mitral stenosis, hypertrophic obstruction cardiomyopathy, pulmonary stenosis) are at high risk for complications.
- Patients with moderate/severe native or recurrent aortic coarctation are at risk for aortic dissection/rupture, as well as increased fetal risk of compromised placental blood supply. If berry aneurysms present, the risk of cerebral hemorrhage is increased:
- Most mild to moderate CHDs add little risk during pregnancy.
- For most women, risk of CHD in neonate is low.
- Management of pregnant women with prosthetic valves is a difficult issue. The 2006 AHA/ACC have described using 1 of 3 reasonable anticoagulation regimens with informed consent:
- Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) or unfractionated heparin (UFH) between 6 and 12 wk gestation and close to term with warfarin at other times
- Careful dose-adjusted UFH throughout pregnancy
- Adjusted dose LMWH throughout pregnancy. The risk of warfarin embryopathy is ~4–10% and may be related to maternal dose with the lowest risk at <5 mg/d.
Patient Monitoring 
Close regular visits with both primary care physician and a cardiologist trained in congenital heart disease
PATIENT EDUCATION 
- The patient must be educated as to the particular risks and limitations of his or her type of congenital heart disease.
- Activity:
- The degree of exercise that is safe for an individual patient depends on the nature of the underlying congenital lesion. Lesions that are at least moderate risk for strenuous exercise:
- Cardiomyopathy
- Various coronary artery anomalies
- Moderate to severe aortic stenosis
- Cyanotic heart disease
- History of serious arrhythmia
PROGNOSIS 
Depends on the severity of the underlying lesion.
Outline
CODES
ICD9
746.9 Unspecified congenital anomaly of heart
SNOMED
13213009 congenital heart disease (disorder)

 1 of the following:
1 of the following:
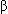 -blockade).
-blockade).