DESCRIPTION 
- Syncope is defined as a sudden transient loss of consciousness and postural tone with recovery of sensory perception shortly thereafter (<1 min).
- Associated physical trauma to the affected patient as a result of the episode is common.
- Consciousness usually returns with assumption of the supine position.
- Episode reflects a transient decrease in cerebral perfusion pressure.
- Rarely life-threatening in children and adolescents
- System(s) affected: Cardiovascular, Neurologic, Musculoskeletal
- Synonym(s): For neurocardiogenic syncope, vasovagal, common faint, neurally mediated, and benign syncope
EPIDEMIOLOGY 
- Represents 3% of emergency room visits and 6% of hospitalizations for adults in the U.S.
- Far less frequent in childhood
- Predominant age: Uncommon in children; increasing frequency through adolescence
- Predominant sex: Male = Female
Incidence 
- ~20% of children will have a syncopal episode by age 15.
- Larger percentage will have presyncopal sensations.
Prevalence 
Not well described in children
RISK FACTORS 
- For neurocardiogenic syncope: Prolonged recumbency, physical exhaustion, and pregnancy
- Breath-holding spells in infancy are usually neurocardiogenic in nature.
- For other forms of syncope: Presence of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome on resting EKG, arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia (ARVD), prolongation of the QT interval on EKG or family history of such, family history of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT), presence of massive ventricular hypertrophy or family history of sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), or serious electrolyte abnormalities
Pregnancy Considerations 
Represents a risk factor for neurocardiogenic syncope in adults
Genetics 
Variable depending on etiology
GENERAL PREVENTION 
For patients with neurocardiogenic syncope, recognition of signs and symptoms preceding a syncopal episode will often allow prevention of such episodes.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 
Common pathway for all forms of neurocardiogenic syncope is stimulation of the medullary vasodepressor region via the Bezold-Jarisch reflex.
ETIOLOGY 
- Most common etiology is neurocardiogenic (23–93% of all childhood syncope)
- Major forms of neurocardiogenic form include vasodepressor, cardioinhibitory, and mixed response.
- Other potential etiologies include bradycardias (sinus bradycardia or atrioventricular block), serious ventricular arrhythmias (eg, long QT syndrome, CPVT, ARVD), supraventricular arrhythmias, or congenital lesions associated with reduced antegrade flow such as aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, coronary arterial anomalies, severe pulmonary stenosis, and cardiac tumors.
Outline
Most common signs and symptoms:
- Light-headedness or visual changes are often noted prior to loss of consciousness (neurocardiogenic).
- When neurocardiogenic in etiology, consciousness usually returns rapidly with assumption of supine position.
- When syncope is due to arrhythmogenic mechanism (eg, long QT syndrome (LQTS), supraventricular tachycardia, and ventricular arrhythmias), often preceded by palpitations or rapid or irregular heart beat; length of syncopal period may be longer than neurocardiogenic.
- For patients with syncope due to arrhythmia, EKG/Holter monitoring may offer clues to etiology such as presence of WPW, ventricular or atrial ectopy, or prolongation of the QT interval.
History 
- Neurocardiogenic (vasovagal, neurally mediated, common faint)
- Commonly seen on hot/humid day, on rapidly arising from supine or seated position, in setting of poor nutrition or hydration
- Standing upright for long periods with venous pooling in lower extremities
- History of light-headedness with arising from supine position
- Positive family history of neurocardiogenic syncope often present
- Syncope with exercise is atypical for neurocardiogenic syncope and demands further testing beyond physical exam and history.
Physical Exam 
- For patients with neurocardiogenic syncope, presence of orthostatic changes should be assessed, with this exception: Physical exam is often not useful in diagnosis.
- Patients with congenital heart defects can have multiple findings on auscultation (see topics on specific heart defects).
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION 
- EKG:
- Atrial and ventricular ectopy may be noted.
- Presence of ventricular preexcitation (eg, WPW) should be assessed.
- Atrioventricular conduction should be reviewed (PR interval).
- Assessment of precordial voltages and ST-T wave changes in assessing for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy should be made (may be more sensitive than even ECG for this diagnosis).
- QTc interval should be measured in all cases.
- 24-hr ambulatory Holter should be screened for ectopy or intermittent preexcitation.
- Home event recording can be useful to detect infrequent arrhythmic events.
- Echo:
- Should be considered in many syncopal children, particularly with a history suggesting a cardiac etiology, an abnormal physical exam, family history of congenital heart disease (eg, HCM, aortic stenosis) or abnormal EKG.
- Head-up tilt-table test:
- Rarely performed in cases where history and etiology are not clear. Test can be repeated with isoprenaline infusion, although specificity decreases with this addition.
- Electrophysiologic study:
- Performed in all patients with syncope and WPW to assess risk characteristics of accessory pathway; otherwise, performed when the etiology is unclear and arrhythmia is suspected either by history or common association (eg, tetralogy of Fallot)
- Exercise stress study:
- Should be performed in all patients with exercise-induced syncope, as well as in patients with activity-related arrhythmias; often used to assess ventricular ectopy response to high-catechol state in patients with ventricular arrhythmias
Lab 
- CBC and electrolytes (including magnesium, calcium, and glucose); blood and urine for toxicology in cases of potential ingestion or illicit drug use
- Genetic testing is successful in identifying ~75% of patients with LQTS; all genetic mutations have not, however, been identified thus far. Genetic testing for CPVT, HCM, and ARVD is also available all patients with these conditions will not be identified.
Imaging 
Echo:
- Used primarily to rule out congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathies and pulmonary HTN; also useful to assess ventricular function
Diagnostic Procedures/Surgery 
- Cardiac catheterization:
- May be necessary to diagnose congenital heart disease
- RV angiography may help in diagnosis of arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia (although not very sensitive); biopsy also may be useful to make this diagnosis.
- Cardiac MRI:
- Demonstrated relatively sensitive for diagnosis of ARVD and increasingly helpful in quantitative follow-up of patients with cardiomyopathies.
Pathological Findings 
For various congenital heart lesions, refer to specific AHA Cardiac Consult Book topics.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 
Neurologic disorders (eg, seizure disorder, neuropathies, brain arteriovenous malformations), metabolic disorders (eg, diabetic ketoacidosis), anemia or ingestions/illicit drug usage
Outline
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS 
- Close regular visits for assessment of symptoms and change in such with therapy is indicated.
- Follow-up for various other conditions causing syncope other than neurocardiogenic are reviewed in individual topics on separate conditions.
Patient Monitoring 
Close regular visits for assessment of symptoms and change in such with therapy is indicated.
DIET 
For patients with neurocardiogenic syncope, high-salt diets with adequate hydration are indicated.
PATIENT EDUCATION 
- Educate patients with neurocardiogenic syncope to appreciate and note the anticipatory feelings of light-headedness that precede syncopal episodes in order to take appropriate actions (supine position, head between knees, etc.) to avoid syncope.
- For other conditions, understanding the importance of compliance with medical regimen is critical.
- Activity:
- For some patients, moderation of exercise may be indicated.
- Certain LQTS patients may have episodes of torsade de pointes triggered by high catecholamine level activities, and in these patients activity that is associated with high catecholamine levels should be curtailed.
- Prevention:
- For patients with neurocardiogenic syncope, recognition of signs and symptoms preceding a syncopal episode will often prevent such episodes.
PROGNOSIS 
- For patients with neurocardiogenic syncope, symptoms usually improve as patients age, with fewer episodes in late adolescence and early adulthood. This may represent self-education at avoidance of activities that induce episodes or recognition of syncopal prodrome with subsequent appropriate preventive measures.
- Arrhythmia course is highly variable and is largely related to efficacy of drug or other (eg, catheter ablation, AICD) therapy.
- Incidence of atrial arrhythmias following Fontan or Mustard/Senning palliation for congenital heart disease increases with time from operation. Episodes or recognition of preceding symptom complexes with subsequent appropriate preventive measures.
COMPLICATIONS 
- Bodily musculoskeletal injury due to falls is common.
- Brain injury due to hypoperfusion of the brain in the setting of prolonged, severe arrhythmias can occur.
Outline
CODES
ICD9
780.2 Syncope and collapse
SNOMED
271594007 syncope (disorder)

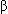 -Blockade may be efficacious in some patients with this disorder.
-Blockade may be efficacious in some patients with this disorder.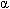 -Adrenergic stimulation (eg,
-Adrenergic stimulation (eg,