DESCRIPTION 
- Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is the rapid, disorganized, and asynchronous contraction of ventricular muscle.
- On the surface EKG, it is characterized by the absence of clearly defined QRS complexes.
- VF represents the final common pathway for death in most patients who experience out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
- Its rate of recurrence is on the order of 30% in the 1st year in successfully resuscitated patients.
- Much of the discussion of ventricular tachycardia (VT; see Arrhythmias, Ventricular Tachycardia) is relevant to VF.
- Synonym(s): Cardiac arrest (refers to collapse due to VT or fibrillation); sudden death (VT followed by VF is usual cause of sudden, unexpected death)
Pregnancy Considerations 
May exacerbate any arrhythmia, and is not uncommon in long QT syndrome
EPIDEMIOLOGY 
- ~350,000 sudden, unexpected, arrhythmic cardiac deaths occur each year in the U.S.
- The prevalence is variable and depends on the presence or absence of structural heart disease.
- Persons of any age can be affected, but the incidence of VF increases with age because structural heart disease, especially coronary artery disease, is the most common substrate and is more frequently present as we age.
- Although VF is not specifically a genetic disease, there is a genetic component, as in congenital long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia.
- Cardiomyopathies, both hypertrophic and dilated, are associated with VT and VF.
RISK FACTORS 
- Same as in coronary artery disease (cigarette use, hyperlipidemia, and HTN)
- Prior MI with or without residual ischemia
- Abnormal LV function (ie, depressed LV ejection fraction, dilated or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy)
- EKG abnormalities:
- EKGs of VF are rarely recorded because efforts are directed at resuscitation during the arrhythmia.
- Rhythm strips show irregular and disorganized ventricular activity; VF is often preceded by VT.
- The baseline EKG may show nonspecific abnormalities such as nonsustained VT, LV hypertrophy, nonspecific ST-T wave changes, intraventricular conduction delays, increased QT dispersion, T-wave alternans, decreased heart rate variability. In specific syndromes, signature findings (long QT in long QT syndrome,
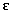 wave in arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia, incomplete right bundle–branch block with ST elevation in leads V1 and V2 in Brugada syndrome).
wave in arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia, incomplete right bundle–branch block with ST elevation in leads V1 and V2 in Brugada syndrome).
- Very rarely, VF will spontaneously terminate.
- Inducible VT in a high-risk patient (after MI, low LV ejection fraction)
ETIOLOGY 
- Coronary artery disease (with or without acute MI)
- Myocardial scar from any cause (most commonly coronary artery disease, but also any structural heart disease and surgical scars)
- Cardiomyopathy (dilated, hypertrophic, arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia)
- Ischemia
- Drug toxicity: Includes traditional antiarrhythmic drugs such as class IC agents in coronary artery disease, QT prolonging drugs (torsade de pointes VT)
- Congenital:
- Diseases involving the ventricles (eg, tetralogy of Fallot)
- Long QT syndromes
- Valvular heart disease (eg, aortic stenosis)
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with rapid ventricular preexcitation during atrial fibrillation
- Myocarditis
- Electrolyte and acid–base abnormalities (hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis)
- Primary electrical disease (idiopathic, Brugada syndrome, nocturnal death in Asians)
COMMONLY ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS 
See list of etiologies and risk factors for VF.
Outline
Signs and symptoms:
- Cardiac arrest
- Syncope, sometimes with seizure activity
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION 
- ECG (MI)
- Electrophysiologic study
- Pathology: Depends on substrate, including coronary artery disease, any cause of myocardial fibrosis (cardiomyopathy, trauma), fibroadipose infiltration of the myocardium (arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia), or none (Brugada syndrome. Long QT syndrome)
Imaging 
- ECG (to evaluate cardiomyopathy, localized wall motion abnormalities such as in coronary artery disease)
- Coronary and LV angiography
- Cardiac MRI (may be useful in diagnosing arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia and infiltrative diseases)
- Exercise test with perfusion imaging (to assess ischemia)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 
EKG/monitor shows rapid and disorganized ventricular electrical activity. There is very little that can be confused with VF, other than artifact (eg, when EKG leads have become dislodged from their positions).
Outline
ADDITIONAL TREATMENT
General Measures 
- Electrical defibrillation is the only definitive, acute treatment.
- Treat underlying heart disease, especially ischemia.
- Treat reversible causes (withdraw toxic drugs, correct electrolyte disturbances).
SURGERY 
- VF is not treated by surgery per se.
- Surgery can be used to correct and/or treat reversible causes of VF, such as coronary artery disease and aortic stenosis.
- The Antiarrhythmics Vs. Implantable Defibrillators (AVID) Trial showed that survivors of cardiac arrest have a greater survival chance when treated with an ICD compared with an antiarrhythmic drug.
- In the absence of a reversible cause or reasons to not implant an ICD, one should be offered.
IN-PATIENT CONSIDERATIONS
Admission Criteria 
- The resuscitation rate in the field is usually <10%.
- If a survivor reaches the hospital, admission is obviously the only option. Even survivors to admission still have a high in-hospital mortality rate and often disability if they are discharged.
Outline
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS
Patient Monitoring 
- Patients are followed according to the needs dictated by the cause of their VF.
- Reversible causes of VF must be treated.
- If drug therapy is chosen, assess compliance, drug levels, effect on ECG, and changes in myocardial substrate.
- Device follow-up if ICD chosen
DIET 
Choose diet appropriate for underlying heart disease (low-cholesterol if coronary artery disease, low-sodium if CHF, calorie-restricted if diabetic).
PATIENT EDUCATION 
- For patients with genetic syndromes, inform regarding need for screening of family members.
- For patients with long QT syndrome, educate regarding drugs to avoid (www.qtdrugs.org), and for those with the congenital form avoidance of precipitating causes of torsade de pointes VT.
- With regard to specific therapies such as the ICD and drugs with potential organ toxicity (eg, amiodarone), specialized information must be made available.
- Activity:
- For VF related to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, exercise is restricted. Similarly, patients with aortic stenosis (presumably awaiting valve replacement or repair) should not exercise while awaiting surgery.
PROGNOSIS 
Outcome depends on underlying heart disease and comorbid conditions. For patients with VF and a structurally normal heart, prognosis is better than if structural heart disease is present. However, the risk for recurrence persists.
Outline
CODES
ICD9
427.41 Ventricular fibrillation
SNOMED
71908006 ventricular fibrillation (disorder)
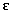 wave in arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia, incomplete right bundle–branch block with ST elevation in leads V1 and V2 in Brugada syndrome).
wave in arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia, incomplete right bundle–branch block with ST elevation in leads V1 and V2 in Brugada syndrome).
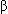 -Blockers, to treat ischemia, and as prophylaxis in congenital long QT syndrome
-Blockers, to treat ischemia, and as prophylaxis in congenital long QT syndrome