DESCRIPTION 
Hurler syndrome is the most severe phenotype within a spectrum of lysosomal storage disorders known as mucopolysaccharidosis I due to deficiency of the enzyme 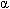 -L-iduronidase. Current terminology applies the term severe MPSI for what has been known as Hurler syndrome and attenuated MPS I for Hurler-Scheie and Scheie syndromes.
-L-iduronidase. Current terminology applies the term severe MPSI for what has been known as Hurler syndrome and attenuated MPS I for Hurler-Scheie and Scheie syndromes.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Incidence 
Incidence is ~1/100,000 live births. The majority MPS I are the severe form (50–80%), although that may be related to a higher rate of diagnosis in the severe form vs. attenuated forms.
RISK FACTORS
Genetics 
Autosomal recessive, caused by 1 of 110 known mutations in IDUA gene, localized on chromosome 4p16.3. The specific mutation is believed to determine phenotype.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 
- Patients are unable to degrade the glycosaminoglycans dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate which provide structural support of the extracellular matrix and cartilaginous structures, including heart valves, joints.
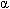 -l-iduronidase enzyme deficiency results in the increase of both heparan and dermatan sulfate in the interstitium.
-l-iduronidase enzyme deficiency results in the increase of both heparan and dermatan sulfate in the interstitium.- Cardiomyopathy and valvar insufficiency occur as glycosaminoglycan accumulates in the myocardium, expands the spongiosa of cardiac valves, and proliferates within the myointima of the epicardial coronary arteries.
- The increase in undegraded glycosaminoglycans results in increased ventricular wall thickness, systolic and diastolic dysfunction with the clinical picture of an infiltrative restrictive cardiomyopathy and CHF.
- Diffuse narrowing of the coronary arteries may occur rather than the focal disease seen in atherosclerotic disease and may result in MI.
ETIOLOGY 
Genetic; caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme 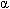 -l-iduronidase
-l-iduronidase
Outline
History 
- Afflicted individuals appear normal at birth, and are typically diagnosed at 6 mo–2 yr of age depending on the severity of the phenotype.
- Patients with the severe phenotype (Hurlers) usually die of obstructive airway symptoms and respiratory infection within the 1st decade of life.
- Cardiac involvement usually presents as premature coronary artery disease with MI, pulmonary HTN with hypoxemia, left-sided valvular (mitral and aortic) insufficiency, pseudohypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and endocardial fibroelastosis, CHF, and also various conduction abnormalities.
Physical Exam 
- Infants with Hurler syndrome usually present in the first 2 yrs after birth with severe mental retardation, hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal deformities, and corneal clouding.
- Progressive coarsening of facial features, short stature
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION
Lab 
- Elevated concentrations of heparan and dermatan sulfate in the urine are sensitive for detecting the enzyme defect but are not a reliable indicator of severity.
- Definitive diagnosis is based on deficient
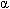 -l-iduronidase activity in leucocytes, fibroblasts, serum, or blood. Prenatal diagnosis is based on enzyme testing or, if the family mutation is known, DNA analysis.
-l-iduronidase activity in leucocytes, fibroblasts, serum, or blood. Prenatal diagnosis is based on enzyme testing or, if the family mutation is known, DNA analysis.
Imaging 
- Echo is used to estimate cardiac involvement by assessing LV wall thickness, valve function, and diastolic and systolic function.
- A radiographic skeletal survey is recommended and will demonstrate a characteristic MPS pattern known as dysostosis multiplex.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 
Outline
- Multidisciplinary team evaluation determines phenotype and assesses development to determine risk/benefits of therapy.
- Hematopoietic stem-cell (HSCT) and umbilical cord-blood transplantation effective in stabilizing the neurologic condition, increasing life span, allowing regression of myocardial wall involvement, and reducing hepatosplenomegaly.
- The risks of transplant are high and currently recommended primarily for children
 2 yr with minimal neurologic involvement (developmental quotients
2 yr with minimal neurologic involvement (developmental quotients  70) in whom maximum benefit is expected.
70) in whom maximum benefit is expected. - HSCT does not prevent progression of heart valve involvement and only stabilizes neurologic involvement.
SURGERY
Some case reports of aortic and mitral valve surgery
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS
Patient Monitoring 
Annual cardiac evaluations using echo recommended to assess for valvular disease, heart failure, cor pulmonale, and cardiomyopathy
DIET 
No restrictions
PATIENT EDUCATION 
Activity: Limited
PROGNOSIS 
Most patients with the severe MPS I phenotype (Hurlers) die before age 10 yr, usually of respiratory complications. Myocardial involvement has been demonstrated to regress with treatment (HSCT or ERT).
COMPLICATIONS 
Respiratory failure, CHF
Outline
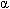 -L-iduronidase. Current terminology applies the term severe MPSI for what has been known as Hurler syndrome and attenuated MPS I for Hurler-Scheie and Scheie syndromes.
-L-iduronidase. Current terminology applies the term severe MPSI for what has been known as Hurler syndrome and attenuated MPS I for Hurler-Scheie and Scheie syndromes.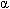 -l-iduronidase enzyme deficiency results in the increase of both heparan and dermatan sulfate in the interstitium.
-l-iduronidase enzyme deficiency results in the increase of both heparan and dermatan sulfate in the interstitium.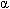 -l-iduronidase
-l-iduronidase
 2 yr of age, patients with neurologic impairment (development quotient
2 yr of age, patients with neurologic impairment (development quotient  70) and for those with the attenuated phenotypes.
70) and for those with the attenuated phenotypes.