Procoagulant Forces (Red) and Natural Anticoagulant/Fibrinolytic Forces (Green) and Diagrammed Dashed Lines Indicated an Inhibitory Effect. Acquired Risk Factors are Presented in Blue Boxes With White Lettering and Arrows Indicating the Mechanism for the Hypercoagulable Effect. “X’S” Denote a Specific Block in a Pathway. Note that Some Acquired Risk Factors Have Multiple Effects; See Text for Full Details. Cpb, Cardiopulmonary Bypass; DDAVP, Desmopressin; Dic, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation; Tf, Tissue Factor; Tfpi, Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor.
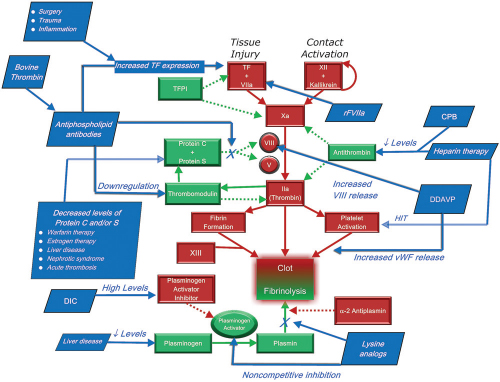
(From Sniecinski RM, Hursting MJ, Paidas MJ, et al. Etiology and assessment of hypercoagulability with lessons from heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Anesth Analg. 2010;112:46-58.)
Procoagulant forces (red) and natural anticoagulant/fibrinolytic forces (green) and diagrammed. Dashed lines indicated an inhibitory effect. Acquired risk factors are presented in blue boxes with white lettering and arrows indicating the mechanism for the hypercoagulable effect. “X’s” denote a specific block in a pathway. Note that some acquired risk factors have multiple effects; see text for full details. CPB, cardiopulmonary bypass; DDAVP, desmopressin; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; TF, tissue factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor.