Fibrinogen is Converted to Fibrin that Polymerizes by the Action of Thrombin The Electron Micrograph Shows a Fibrin Clot With Red Blood Cells Trapped. Platelets Also are Critical to Fibrin Formation, but They are 8 to 10 Microns and Not Visible in the Photo. Fibrinogen Receptors on the Platelet Surface (Called Iib/Iiia Receptors) Facilitate the Lattice Network of Fibrin Formation. Factor XIII, a Transglutamase, is Also Important for Cross-Linking the Fibrin Clot to Create a Stronger Clot that is Resistant to Fibrinolysis.
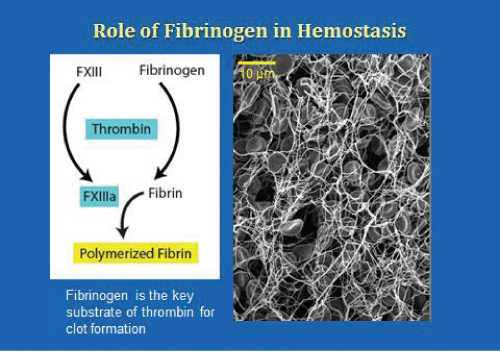
(Modified from Tanaka KA, Key NS, Levy JH. Blood coagulation: hemostasis and thrombin regulation. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:1433-1446.)
Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin that polymerizes by the action of thrombin. The electron micrograph shows a fibrin clot with red blood cells trapped. Platelets also are critical to fibrin formation, but they are 8 to 10 microns and not visible in the photo. Fibrinogen receptors on the platelet surface (called IIb/IIIa receptors) facilitate the lattice network of fibrin formation. Factor XIII, a transglutamase, is also important for cross-linking the fibrin clot to create a stronger clot that is resistant to fibrinolysis.