A Simplified Diagram of the Effects of a Decrease in Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation (v) on Arterial Oxygenation (a)
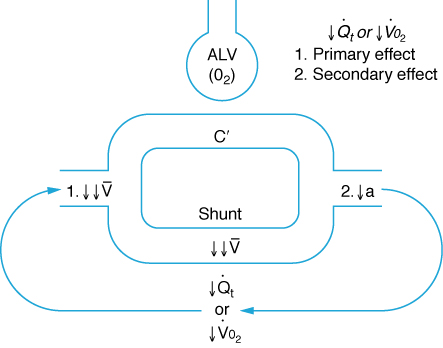
(From Nunn’s Applied Respiratory Physiology. 7th ed. Edinburgh, United Kingdom: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010, with permission.)
Mixed venous blood passes either though ventilated lung regions (ALV), where it is oxygenated in the pulmonary capillaries (c′) or through nonventilated (shunt) lung regions. A decrease in mixed venous oxygen due to either a decrease in cardiac output (Qt) or an increase in oxygen consumption (Vo2) will pass through the pulmonary shunt and result in a fall in arterial oxygenation.