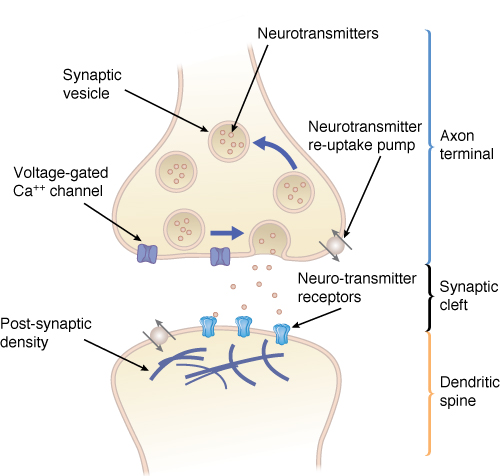
Basic Structure of the Synapse
(From Hughes MA, Glass PSA, Jacobs JR. Context-sensitive half-time in multicompartment pharmacokinetic models for intravenous anesthetic drugs. Anesthesiology. 1992;76:334-341, with permission.)
The signal arrives at the axon terminal, where it causes the release of neurotransmitters into the synapse. These cross the synaptic cleft, where they may or may not result in a propagation of the signal. Many synapses simply render the postsynaptic cell excited or inhibited without actually triggering an action potential.