Mechanism of Action of the Three Classes of Calcium Channel Blockers
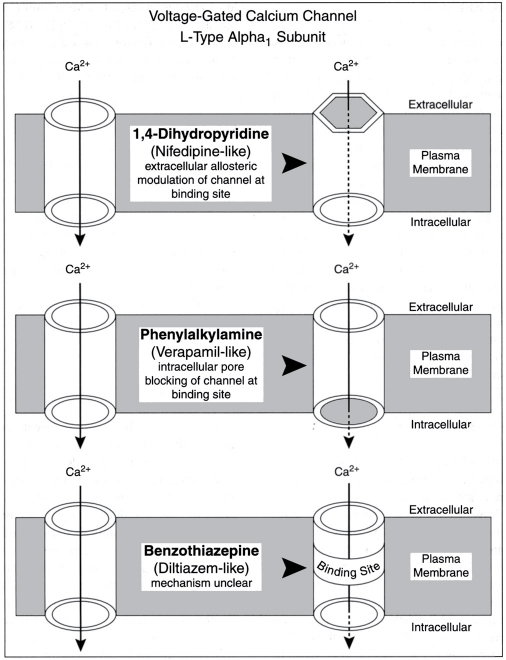
(From Kanneganti M, Halpern NA. Acute hypertension and calcium-channel blockers. New Horiz. 1996;4:19-25, with permission.)
Calcium enters the cytosol (black arrows) of the vascular smooth muscle cell either from the extracellular space through the plasma membrane (top of diagram) or from the intracellular storage areas. The primary entry sites for calcium ions are the voltage-gated channels.