The Second Gas Effect is the Accelerated Increase in the Alveolar Concentration of aSecond Gas, Halothane (Haloth), Toward the Inspired (Fa/Fi) in the Presence of a High Inhaled Concentration of the First Gas (N2o)
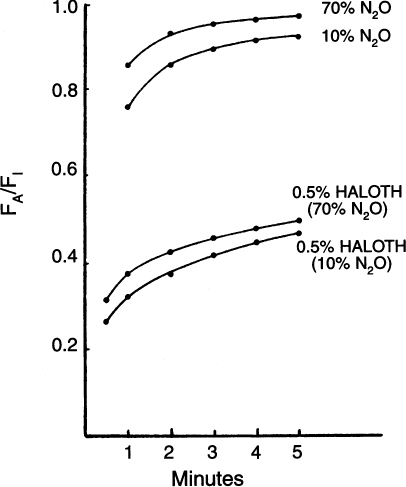
(From Epstein RM, Rackow H, Salanitre E, et al. Influence of the concentration effect on the uptake of anesthetic mixtures: the second gas effect. Anesthesiology. 1964; 25:364-371, with permission.)
The impact of the inhaled concentration of an anesthetic on the rate at which the alveolar concentration increases toward the inspired (FE/FI) is known as the concentration effect.