Effect of the Mode of Ventilation on the Rate of Increase of the Alveolar Concentration (Fa) of Halothane Toward the Inspired Concentration (Fi) As Determined in an Animal Model Negative-Feedback Inhibition of Spontaneous Ventilation (A) Limits the Fa/Fi to 0.6 for All the Inspired Concentrations of Halothane. The Positive-Feedback Effect of Controlled Ventilation (B) Results in Ratios of the Fa/Fi that Approach 1.0 and Excessive Depressant Effects of Halothane on the Cardiovascular System at the Higher Inspired Concentrations of the Anesthetic. (Data are Mean ± Sd.)
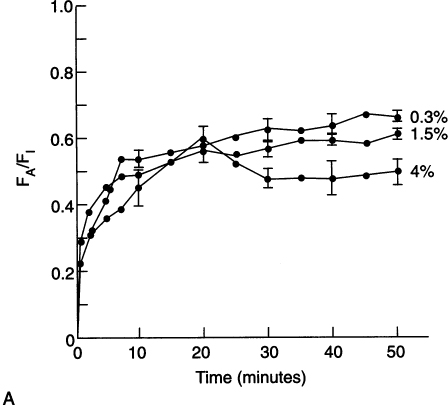
(From Gibbons RT, Steffey EP, Eger EI II. The effect of spontaneous versus controlled ventilation on the rate of rise in the alveolar halothane concentration in dogs. Anesth Analg. 1977;56:32-37, with permission.)
Effect of the mode of ventilation on the rate of increase of the alveolar concentration (FA) of halothane toward the inspired concentration (FI) as determined in an animal model. Negative-feedback inhibition of spontaneous ventilation (A) limits the FA/FI to 0.6 for all the inspired concentrations of halothane. The positive-feedback effect of controlled ventilation (B) results in ratios of the FA/FI that approach 1.0 and excessive depressant effects of halothane on the cardiovascular system at the higher inspired concentrations of the anesthetic. (Data are mean ± SD.)
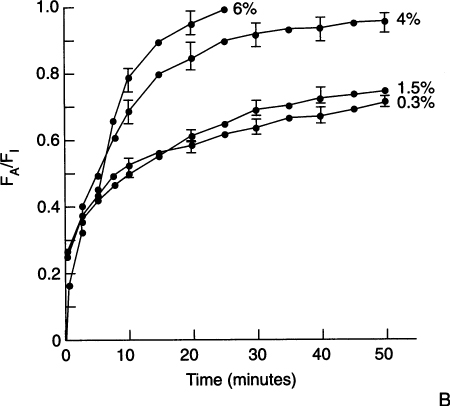
(From Gibbons RT, Steffey EP, Eger EI II. The effect of spontaneous versus controlled ventilation on the rate of rise in the alveolar halothane concentration in dogs. Anesth Analg. 1977;56:32-37, with permission.)
Effect of the mode of ventilation on the rate of increase of the alveolar concentration (FA) of halothane toward the inspired concentration (FI) as determined in an animal model. Negative-feedback inhibition of spontaneous ventilation (A) limits the FA/FI to 0.6 for all the inspired concentrations of halothane. The positive-feedback effect of controlled ventilation (B) results in ratios of the FA/FI that approach 1.0 and excessive depressant effects of halothane on the cardiovascular system at the higher inspired concentrations of the anesthetic. (Data are mean ± SD.)