
Definition
- Sinus arrest-a disorder of impulse formation caused by slowing or cessation of spontaneous sinus nodal automaticity; failure of the SA node to initiate an impulse at the expected time. P-P interval does not equal a multiple of basic P-P interval.
- Sinoatrial block-a disorder of impulse conduction; an impulse formed within the sinus node fails to depolarize the atria or does so with delay; most commonly the basic rhythmicity of the sinus node is not disturbed and the duration of the pause is a multiple of the basic P-P interval. Classified into first-, second-, and third-degree SA block (similar to degrees of AV block). Difficult to diagnose first- and third-degree SA block from ECG. Second-degree SA block most common: Mobitz type I (Wenckebach) SA block-P-P interval progressively shortens prior to a pause; duration of pause is less than two P-P cycles; Mobitz type II SA block-duration of pause occurring after a sinus beat is exact multiple (two, three, or four times normal) of basic P-P interval.
ECG Features
- A normal P wave exists for each QRS complex with a pause equal to or greater than twice the normal P-P interval; rhythm is regularly irregular or irregular with pauses (Figure 2).
- Junctional or ventricular escape beats-occurs if pauses significantly prolonged. Subsidiary pacemaker takes over rhythm with escape beats normally from AV junctional tissue or Purkinje fibers; intermittent absence of P waves noted or P waves may be negative and precede, be superimposed on or follow the QRS complexes.
- Surface ECG cannot differentiate sinus arrest from block in the dog because of normal R-R interval variation (sinus arrhythmia).
Pathophysiology
- Sympathetic and parasympathetic influences can alter spontaneous sinus node depolarization; vagal stimulation of acetylcholine, which binds to SA nodal receptor sites, can slow automaticity of the sinus node by reducing the slope of phase 4 depolarization; sympathetic stimulation releases norepinephrine that binds to
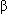 1 receptors on the SA node, enhancing spontaneous SA nodal discharge rate.
1 receptors on the SA node, enhancing spontaneous SA nodal discharge rate. - Post-drive inhibition phenomenon occurs when sinus arrest follows a run of ectopic beats. The sinus node requires a warming-up period until the usual rate of automaticity is reestablished.
- Intrinsic disease of the sinus node may affect the balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic efferent traffic to the SA node and its spontaneous discharge rate.
- Duration of sinus arrest may be long and possibly irreversible when the sinus node is suppressed by an ectopic tachycardia, particularly with severe underlying heart disease. Persistent sinus arrest not due to any drug often indicates SSS.
Systems Affected
Cardiovascular-clinical signs of weakness or syncope may appear if sinus arrest or block causes sufficiently long periods (generally 5 seconds or longer) of ventricular asystole with no escape beats initiated by latent pacemakers.
Genetics
- Seen in purebred pugs with hereditary stenosis of the bundle of His.
- Seen in female miniature schnauzers predisposed to SSS. Is the most common arrhythmia in miniature schnauzers with SSS.
- Congenitally deaf Dalmatian coach hounds often have abnormal SA node and multiple atrial arteries. May be a genetic component to the cause of SSS in those breeds predisposed (see below).
Incidence/Prevalence
- Normal incidental finding in brachycephalic breeds of dogs in which inspiration causes a reflex increase in vagal tone.
- Common in dog breeds predisposed to SSS.
- Uncommon in cats.
Geographic Distribution
N/A
Signalment
Species
Dogs and cats
Breed Predilections
- Brachycephalic breeds.
- Breeds predisposed to SSS (e.g., miniature schnauzers, dachshunds, cocker spaniels, pugs, boxers and West Highland white terriers).
Mean Age and Range
If associated with SSS, generally middle-aged to older animal
Predominant Sex
If associated with SSS, older females
Signs
General Comments
Generally no clinical significance by itself if terminated by sinus node depolarization, or latent pacemakers promptly escape to prevent ventricular asystole.
Historical Findings
- Usually none.
- Signs of low cardiac output (e.g., weakness and syncope) may occur with failure of the SA node to fire on time if no lower pacemaker focus takes over the rhythm.
- Sudden death is possible should prolonged periods of ventricular asystole occur.
Physical Examination Findings
- May be normal.
- Heart sounds following a pause may be louder because the ventricles had longer to fill and eject a larger amount of blood.
- Extremely slow heart rate if arrest or block is prolonged or frequent.
- With significant pathologic cardiac disease-may be findings consistent with poor cardiac output (e.g., prolonged perfusion time, pale mucous membranes, weak femoral pulses).
Causes
Physiologic
- Vagal stimulation secondary to coughing, pharyngeal irritation
- Ocular or carotid sinus pressure
- Surgical manipulation
Pathologic
- Degenerative heart disease (fibrosis)
- Dilatory heart disease
- Acute myocarditis
- Neoplastic heart disease
- SSS
- Irritation of vagus nerve secondary to thoracic or cervical neoplasia
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Drug toxicity (e.g., digoxin)
Risk Factors
- Certain drugs, including digitalis, quinidine, propranolol, xylazine, acepromazine, hydromorphone
- Respiratory tract disease
- Vagal maneuvers




