
Definition
- Feline hepatic lipidosis->80% of hepatocytes accumulate substantial triglyceride vacuoles that distend the cytosolic compartment, causing canalicular compression, severe cholestasis, and liver dysfunction.
- Untreated-leads to progressive metabolic dysregulation and death.
- Develops secondary to a primary disease or condition causing anorexia or catabolism.
Pathophysiology
- Cats have a unique propensity to accumulate triglyceride filled hepatocellular vacuoles.
- Causal factors-energy and protein deficits; increased peripheral fat mobilization; increased hepatic triglyceride synthesis; impaired hepatic
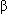 -oxidation of fatty acids; reduced hepatocellular triglyceride exportation.
-oxidation of fatty acids; reduced hepatocellular triglyceride exportation. - Cytosolic triglyceride vacuoles displace organelles to cell periphery, associate with organelle dysfunction, and canalicular compression.
- Hepatic failure-with rare overt HE.
Systems Affected
- Hepatobiliary-severe intrahepatic cholestasis, hepatic dysfunction or failure
- Gastrointestinal-anorexia; vomiting
- Musculoskeletal-peripheral tissue wasting
- Nervous-HE, ptyalism, moribund condition
- Hemic/Lymphatic/Immune-abnormal RBC shapes (poikilocytes), Heinz body hemolysis
- Renal/Urologic-potassium wasting; renal tubule triglyceride accumulation
Incidence/Prevalence
Most common severe feline hepatopathy in North America causing jaundice.
Geographic Distribution
Worldwide
Signalment
Species
Cat, rarely dog (toy breed puppies; also see Glycogen Storage Disease).
Breed Predilection
N/A
Mean Age and Range
Middle-aged adult cats: 8 (1–16 years)
Predominant Sex
N/A
Signs
Historical Findings
- Anorexia, hyporexia, weight loss, sarcopenia
- Jaundice
- Lethargy, weakness progressing to collapse
- Vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation
- Ptyalism: may reflect food aversion or HE
- Neck ventriflexion: weakness, electrolyte depletion: potassium, phosphate; thiamin deficiency
- Abnormalities due to underlying disease
Physical Examination Findings
- Jaundice
- Hepatomegaly
- Dehydration
- Weakness-neck ventriflexion, recumbency
- Ptyalism
- Collapse/Obtunded
- Others, depending on underlying or primary disease; HE (rarely overt)
Causes
“Idiopathic” Hepatic Lipidosis
“Idiopathic” = inappropriate terminology; antecedent health problems are discoverable in >85% of cases causing anorexia or malassimilation; remainder have food deprivation.
Secondary Hepatic Lipidosis
- Primary liver disease-PSVA; CCHS; EHBDO; cholelithiasis; neoplasia
- Gastrointestinal-obstruction; neoplasia (lymphosarcoma); IBD; pancreatitis
- Urogenital disease-renal failure, CIN, lower urinary tract syndrome
- Neurologic conditions: cannot eat
- Infectious diseases-toxoplasmosis; FIP; FIV- or FeLV-related disorders
- Hyperthyroidism
- Vitamin B12 deficiency (may predispose cats to HL)
- Many other systemic conditions or toxins
- Rapid weight loss protocol
Risk Factors
- Obesity
- Anorexia, negative nitrogen balance
- Catabolism or rapid weight loss
- Vitamin B12 deficiency




