
Definition
Refers to a delay in conduction that occurs between atrial and ventricular activation.
Pathophysiology
- Virtually never causes clinical signs.
- May become a more severe AV conduction disturbance in some animals.
- Normally the PR interval tends to shorten with rapid heart rates.
- May be the result of intra-atrial conduction delay (prolongation of the PA interval on surface ECG and simultaneous His bundle electrogram) or delay of conduction within the AV node itself (prolongation of the AH interval on His bundle electrogram).
Systems Affected
Cardiovascular
Genetics
N/A
Incidence/Prevalence
Common
Geographic Distribution
None
Signalment
Species
Dog and cat
Breed Predilections
American cocker spaniel, dachshund, brachycephalic dogs, Persian cats
Mean Age and Range
- May occur in young, otherwise healthy dogs as a manifestation of high vagal tone.
- Intra-atrial conduction delay involving the right atrium may be seen with congenital heart disease, especially atrioventricular septal defects.
- May be noted in aged patients with degenerative conduction system disease, particularly cocker spaniels and dachshunds.
- Persian cats of any age with high vagal tone and in cats of any age with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Signs
Historical Findings
- Most animals are asymptomatic.
- If drug-induced, may have a history of clinical signs related to drug toxicity-anorexia, vomiting, and diarrhea with digoxin; weakness with calcium channel blockers or
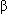 -adrenergic antagonists.
-adrenergic antagonists.
Physical Examination Findings
- Normal-unless also signs of more generalized myocardial disease, drug toxicity, or non-cardiac disease.
Causes
- May occur in normal animals.
- Enhanced vagal stimulation resulting from non-cardiac diseases-usually accompanied by sinus arrhythmia, sinus arrest, and/or Mobitz type I second-degree AV block.
- Pharmacologic agents (e.g., digoxin,
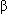 -adrenergic antagonists, calcium channel blocking agents, propafenone, amiodarone,
-adrenergic antagonists, calcium channel blocking agents, propafenone, amiodarone,  2-adrenergic agonists, parasympathomimetic agents [bethanechol, physostigmine, pilocarpine] and severe procainamide or quinidine toxicity).
2-adrenergic agonists, parasympathomimetic agents [bethanechol, physostigmine, pilocarpine] and severe procainamide or quinidine toxicity). - Degenerative disease of the conduction system.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Myocarditis (especially Trypanosoma cruzi, Borrelia burgdorferi, Rickettsia rickettsii).
- Infiltrative diseases (tumors, amyloid).
- Atropine administered intravenously may briefly prolong the PR interval.
Risk Factors
Any condition or intervention that raises vagal tone




