
Definition
Serum potassium concentration <3.5 mEq/L (normal range: 3.5–5.5 mEq/L).
Pathophysiology
- Potassium is primarily an intracellular electrolyte (98% of total body potassium is intracellular); serum levels, however, may not accurately reflect total body concentrations.
- It is predominantly responsible for the maintenance of intracellular fluid volume and required for normal function of many enzymes.
- The resting cellular membrane potential is determined by the ratio of intracellular to extracellular potassium concentration and maintained by the Na+, K+-ATPase pump. Conduction disturbances in susceptible tissues (cardiac, nerve, and muscle) are caused by rapid shifts in this ratio causing myoneural membrane hyperpolarization.
- Hypokalemia can be caused by decreased intake, loss (via the gastrointestinal tract or kidneys), or translocation of potassium from the extracellular to the intracellular fluid space.
Systems Affected
- Neuromuscular-muscle weakness, including skeletal and muscles of respiration.
- Cardiac-electrocardiac changes and arrhythmias.
- Renal-hyposthenuria, nephropathy, and renal failure.
- Metabolic-acid-base balance (metabolic alkalosis); glucose homeostasis.
Signalment
- Dogs and cats with predispositions to increased potassium loss, translocation of potassium, or decreased intake of potassium.
- Young Burmese cats with recurrent hypokalemic periodic paralysis episodes.
Signs
- Generalized muscle weakness or paralysis
- Muscle cramps
- Lethargy and confusion
- Vomiting
- Anorexia
- Carbohydrate intolerance and weight loss
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
- Decreased bowel motility (humans; maybe dogs and cats)
- Hyposthenuria
- Ventroflexion of the neck (cats and dogs)
- Respiratory muscle failure
Causes
Decreased Intake
- Anorexia or starvation
- Administration of potassium-deficient or potassium-free intravenous fluids
- Bentonite clay ingestion (e.g., clumping cat litter)
Gastrointestinal Loss
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Both upper and lower gastrointestinal obstruction; especially pyloric outflow obstruction
Urinary Loss
- Chronic renal disease
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Hypokalemic nephropathy.
- Post-obstructive diuresis
- Dialysis (hemodialysis or peritoneal)
- Intravenous fluid diuresis
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Hypochloremia
- Drugs (loop diuretics, amphoteracin B, penicillins, rattlesnake envenomation)
Translocation (Extracellular to Intracellular Fluid)
- Glucose administration
- Insulin administration
- Sodium bicarbonate administration
- Catecholamines
- Alkalemia
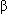 2-adrenergic agonist overdose (e.g., albuterol)
2-adrenergic agonist overdose (e.g., albuterol)- Hypokalemic periodic paralysis (Burmese cats)
- Rattlesnake envenomation (mechanism unknown)
Risk Factors
- Acidifying diets with negligible potassium
- Diuresis or dialysis with potassium-deficient fluids
- Chronic illness (sustained anorexia and muscle wasting)




