Louse (plural: lice) is the common name for members of over 3,000 species wingless insects of the order Phthiraptera.
There are two species of sucking lice: Pediculus humanus and Phthirus pubis (pubic lice, sometimes called “crabs”).
P. humanus is further divided into two subspecies: P. humanus capitis (the head louse) and P. humanus corporis (the body louse).
Head lice spread from human to human; epidemics of head lice are most commonly seen in schoolchildren.
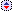
The head louse is wingless insect (2.5 to 3 mm long). They spend their entire life on the human scalp and feed exclusively on human blood.
They are grey in general, but their color varies. After feeding, consumed blood causes the louse body to take on a reddish color (Fig. 29.21).
Head lice occur more often in girls and women than in boys and men; they are unusual in African-Americans, but not in African blacks.
Pediculosis pubis (also known as “crabs” and “pubic lice”) is a disease caused by the pubic louse, P. pubis, a parasitic organism notorious for infesting human pubic hair. The species may also live on other areas with hair, including the eyelashes, causing pediculosis ciliaris.
Infestation usually leads to intense itching in the pubic area.
Head Lice
There are no primary lesions; however, secondary crusts and eczematous dermatitis resulting from scratching may be present.
Nits (louse eggs) are cemented to the hairs (Fig. 29.22).
Pubic Lice
Small living brown lice may be seen at the base of hairs (Fig. 29.23).
Blue macules (maculae ceruleae), thought to result from enzymes present in louse saliva that breakdown bilirubin, may occur on nearby skin in chronic infestations.
Pubic hair, eyebrows, eyelashes, and axillary hair may be infested.
Head Lice (see also Chapter 9: Hair and Nail Disorders)
Knowledge of an epidemic at school generally alerts parents or school nurses to look for evidence of lice.
A hair may be plucked and examined for nits using the low power of a microscope.
A nit is attached to the base of a hair shaft when the egg is first laid and remains cemented to the growing hair.
Pubic Lice
Head Lice
|
Outline