Athlete's foot is a very common superficial skin infection caused by a fungus. Those pervasive TV commercials are evidence of just how widespread this problem is.
The fungus that causes athlete's foot is not very contagious, but it tends to grow in a warm, moist, sweaty environment such as that found in shoes or sneakers.
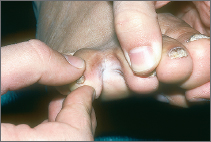
Athlete's foot (tinea pedis) between the toes
There are two main types of athlete's foot: the acute toe web infection, the most common type, and the “moccasin” or “dry” type.
Peeling and sometimes cracking (“fissures”) of the skin between the toes, usually the last two toes, are apparent.
The infection may also be associated with an unpleasant odor.
The peeling and cracking can spread to neighboring toes if the fungus is not treated.
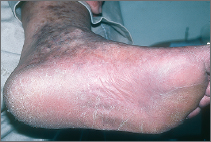
Chronic tinea pedis
Treatment of acute toe web infection
Prevention of acute toe web infection
Decreasing wetness and friction helps. Frequent changes of socks, the use of absorbent powders such as Zeasorb-AF or baby cornstarch, and drying the area with a hair dryer after bathing are preventive.
The fungus that causes athlete's foot is found almost everywhere, so taking special precautions to avoid it may not be worth the effort. Nonetheless, many dermatologists recommend daily washing of the feet, thorough drying between the toes, avoidance of tight footwear, wearing absorbent cotton or synthetic socks, and using antifungal powders in the shoes.
This scaly, sometimes reddish condition appears on the soles of the feet, often both feet. Sometimes it involves the palms; possibly only one hand is affected.
It's usually not very itchy, but sometimes the skin thickens and cracks and becomes painful.
The infection can also involve the toenails; these infections are more difficult to treat.
Be aware that these symptoms and a similar appearance can be a result of other causes such as psoriasis or eczema.
Treatment of the “moccasin” or “dry” type
Treatment, if necessary, generally requires an oral antifungal agent such as _______________, in addition to topical agents such as _______________.
This type of athlete's foot is more difficult to cure than the acute toe web infection.
Recurrence is common after therapy and can lead to long-term infection.
Outline