Si nada de esto ayuda, puede mantener un diario de los alimentos que consume diariamente, seguido por una eliminación gradual de aditivos y ciertos alimentos. Esto a veces ayuda.
Melasma is a type of skin darkening (hyperpigmentation) that is seen most commonly on the face.
It may develop during pregnancy, while taking birth control pills, or during menopause. Sometimes it appears for no obvious reason.
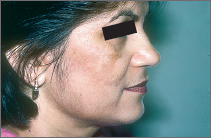
Melasma
Melasma most commonly occurs in women during their reproductive years, particularly in women who have darker complexions and live, or were born, in a sunny climate.
It's seen most often in Asia, the Middle East, South America, Africa, and the Indian subcontinent.
In North America, it's most common among Hispanics, African-Americans, and immigrants from countries in which it's very common.
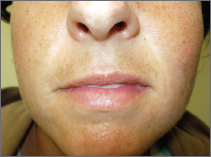
Melasma
Tan or brown spots are seen mainly on the cheeks, jaw, forehead, nose, chin, and above the upper lip.
During pregnancy, the darkening of the skin often appears in the second and third trimesters and usually fades after the end of pregnancy.
It also tends to fade when oral contraceptives are stopped or when sunlight is avoided. (Exposure to sunlight makes it worse.)
Treatment of melasma involves a combination approach with one or more bleaching agents and a cosmetic for camouflage. In addition, sun avoidance and the use of sunblocks are very important.
Bleaching creams are readily available over the counter. Preparations such as the low-strength Ambi and Esoterica contain 2% hydroquinone.
Stronger preparations are available by prescription only. Some contain sunblock, a topical steroid, Retin-A, vitamins C and E, and/or glycolic acid.
Other lightening agents, such as azelaic acid and kojic acid, may be used in addition to hydroquinone. These have been found to help lighten melasma.
All of these preparations should be applied twice a day to areas of darkening only. Slow but gradual lightening is to be expected.
This treatment requires patience during the many months in which lightening agents must be applied.
Without the strict avoidance of sunlight, successful treatments for melasma are doomed to failure.
Sunscreens are essential. They should be broad spectrum, which means that they should protect against both ultraviolet A and ultraviolet B rays. Those containing opaque physical blockers such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide are preferred over chemical sunscreens because of their broader protection. They should be used on a daily basis, whether or not it is sunny.
Chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and laser procedures have also been used to treat melasma.